Thunderstorms are one of nature’s most spectacular displays, with lightning and thunder causing a captivating mix of visual and acoustic effects. But what are thunderstorms and how do they form?
Thunderstorms are an electrical storm that can produce lightning, thunder, heavy rain, intense winds, and hail.
Cumulonimbus clouds, which produce thunderstorms, are tall, dark, and ominous clouds, which easily warn the onlooker of the poor weather that is on the way.
All thunderstorms require three key ingredients:
- An unstable atmosphere (warm and humid air), meaning the air becomes cooler with height.
- Low-level moisture in the atmosphere (high humidity).
- A trigger mechanism that causes air to rise from the surface to form the tall cumulonimbus clouds.
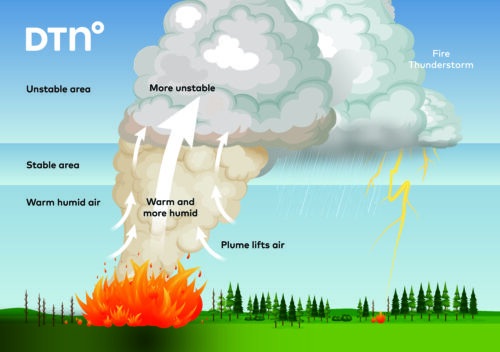
When the sun heats the earth’s surface the air just above the ground starts to warm up. This warm and humid air becomes more buoyant than the cooler and drier air above it, causing the warm surface air to rise.
Cold fronts, lows, troughs, and mountain ranges can all trigger thunderstorms, by lifting air from the surface and sending it high into the atmosphere.
As the rising air travels higher into the atmosphere, water vapor within the air parcel condenses into liquid droplets, causing clouds to form.
These clouds can grow into tall cumulonimbus clouds when the upward motion of air is strong and sustained. This rising air called an updraught, which transports water vapor, super cooled liquid water, and ice crystals sometimes up to ten kilometres into the atmosphere.
As the water droplets and ice crystals travel up in the updraught they bump and crash into each other, becoming larger.
Eventually the water droplets and ice crystals/hail become too heavy to be suspended by the updraught and begin to fall. This initiates a downward current of air, or a downdraught, which brings rain, hail, and gusts of air crashing down towards the ground.
At this stage in a thunderstorm’s lifecycle, the storm becomes mature and this is when hail, heavy rain, lightning and strong winds are most likely to occur.
Some thunderstorms can cause violent downdraughts called downburst or microbursts. These occur when rapidly sinking air containing hail or rain becomes progressively cooler through the process of evaporation.
This cool and dense air rushes towards the ground and spreads out to cause powerful straight-line winds that can cause significant damage. One of these microbursts hit Sydney’s Northern Beaches on December 19, 2021, snapping trees, cutting power lines and ripping rooves off buildings.
A thunderstorm will begin to choke itself when the heavy rain and cool air within the storm replaces the warm humid updraught. This is the weakening phase of a storm when it is dissipating and rainfall begins to ease, however lightning can still be a threat at this stage.
Weatherzone provides our clients with thunderstorm, damaging wind and heavy rainfall forecasting out to 14 days, for more information please contact us at apac.sales@dtn.com.