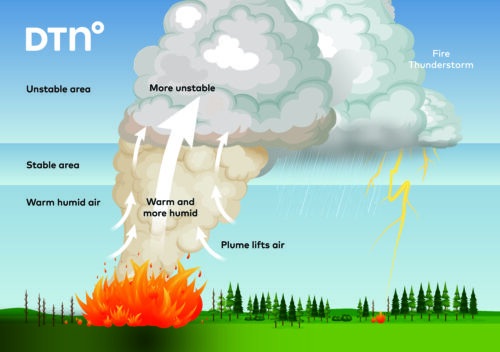
Tropical cyclones are large rotating masses of cloud, rain, thunderstorms and wind that can cause a lot of damage and loss of life. But what is a tropical cyclone and how are they formed?
What is a cyclone?
A tropical cyclone is an intense area of low pressure surrounded by a rotation mass of clouds.
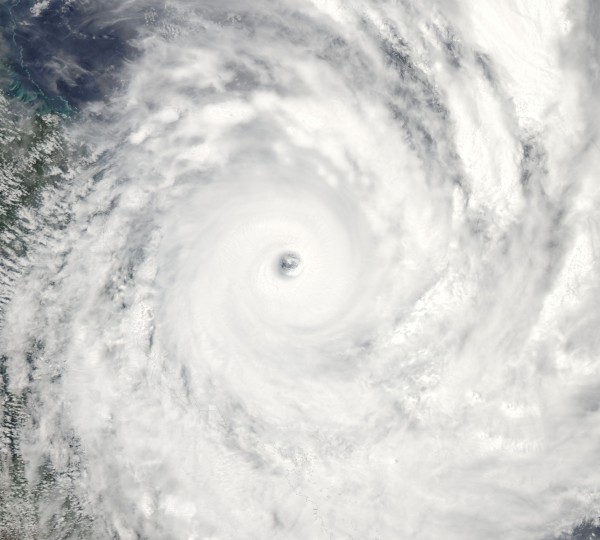
While the eye of a tropical cyclone is often clear and relatively calm, conditions surrounding the eye typically consist of destructive winds, squally rain, thunderstorms and dangerous waves.
Australia rates tropical cyclones using a five-tiered scale based on the following mean wind speeds:
- Category 1: 63 to 88 km/h (typical gusts <125 km/h)
- Category 2: 89 to 117 km/h (typical gusts 125 to 164 km/h)
- Category 3: 118 to 159 km/h (typical gusts 165 to 224 km/h)
- Category 4: 160 to 199 km/h (typical gusts 225 to 279 km/h)
- Category 5: > 200 km/h (typical gusts > 279 km/h)
Image: Severe Tropical Cyclone Yasi near the QLD coast in 2011. Source: NASA
How are tropical cyclones formed?
Tropical cyclones develop from clusters of thunderstorms over tropical oceans. Under the right conditions, these storms can grow and begin to rotate an develop into a closed low pressure system.
If this low pressure system becomes deep enough, it becomes a giant heat engine that draws energy from the warm oceans beneath it.
Once fully-formed, a tropical cyclone consists of towering clouds of rain and thunderstorms surrounding a relatively clear and calm eye. The most violent weather is usually found inside this eye-wall of a tropical cyclone.
As the name suggests, tropical cyclones only form in the tropics because they require warm water of at least 26.5ºC to develop and gain strength. Water this warm is in abundance on either side of the equator and the warmer the sea surface temperature, the stronger the cyclone can get.
Image: Global sea surface temperatures on December 19, 2021. Source: NOAA
On average, we usually see around 10-12 tropical cyclones in the Australia region each year. They are most common near Australia between November and April, although they can develop at any time of year.
Cyclone vs Hurricane vs Typhoon
Tropical cyclones, hurricanes and typhoons are all the same thing. These are simply different names given to tropical cyclones that develop in different parts of the world.
- Tropical Cyclone is used in the Indian Ocean, South Pacific Ocean
- Hurricane is used in the North Atlantic Ocean and North East Pacific Ocean
- Typhoon is used in the North West Pacific Ocean
However, one key difference is that tropical cyclones rotate in a clockwise direction in the southern hemisphere and an anticlockwise direction in the northern hemisphere, regardless of the name.
Tropical cyclones, hurricanes and typhoons also have slightly different thresholds before they are named. These thresholds are determined by the governing meteorological organisations in the relevant part of the world.
For example, a high-end category two tropical cyclone in the South Pacific region is the same strength as a Typhoon in the North West Pacific and a category one hurricane in the North Atlantic region.
Weatherzone forecasts tropical cyclone risk out to 14 days as well as providing consultancy on possible impacts, for more information, please contact us at apac.sales@dtn.com.