A negative Indian Ocean Dipole pattern has started to emerge to the northwest of Australia in the past fortnight, increasing the likelihood of a wet and cloudy winter for much of the country.
What is a negative Indian Ocean Dipole and how does it affect Australia?
The Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) simply refers to an index that measures the difference in sea surface temperatures in two regions on either side of the Indian Ocean.
When the IOD is in a negative phase:
- Warmer-than-average water sits on the eastern side of the equatorial Indian Ocean, near Indonesia.
- Cooler-than-average water sits on the western side of the equatorial Indian Ocean, near the Horn of Africa.
- This sea surface temperature contrast causes more moisture-laden air to flow towards Australia.
- This airborne moisture typically increases rain and cloud cover over Australia, which decreases daytime temperatures across large areas in winter and spring.
Image: Typical sea surface temperature anomalies and associated weather impacts during a negative IOD.
Negative IOD emerging
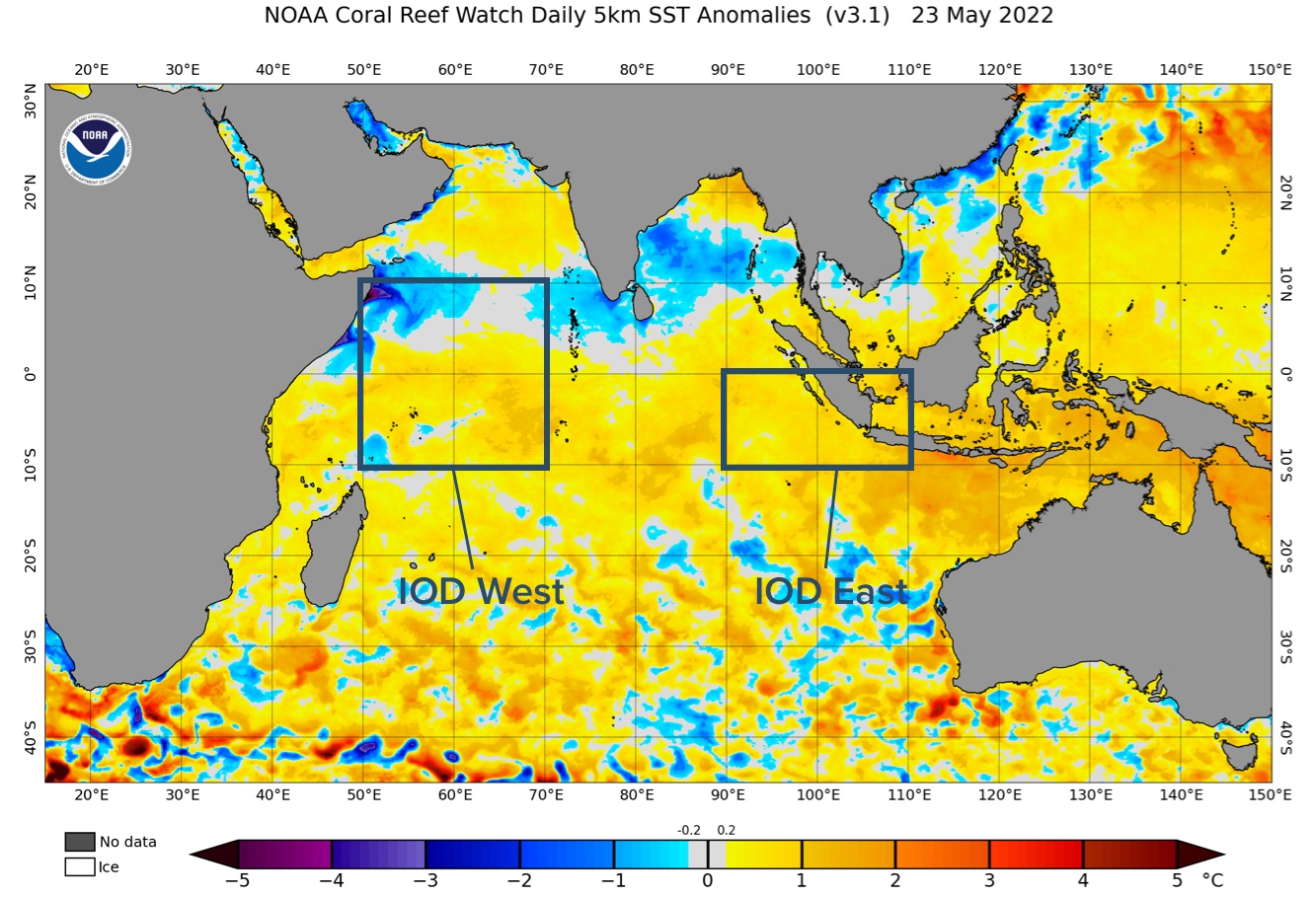
The Bureau of Meteorology will declare a negative IOD event when the IOD index is consistently lower than -0.4 for a prolonged period of time, typically at least eight weeks.
While the IOD is currently officially neutral (average conditions for Australia), the latest weekly IOD value for the week ending on May 22 was minus -0.55. This is the first value below the -0.4 threshold so far this year.
Image: Sea surface temperature anomalies in the Indian Ocean on May 23, 2022. The tow IOD regions (east and west) and annotated using boxes.
All seasonal climate models predict that negative IOD values will continue throughout winter and possibly spring, with most models suggesting that this will be a strong negative IOD event.
What does a negative IOD event mean for Australia?
A negative IOD typically causes the following weather impacts in Australia during winter and spring:
- Above average winter and spring rainfall across parts of southern Australia.
- Increased cloud cover and reduced solar output.
- Stronger and more frequent northwest cloudbands.
- Below average maximum temperatures across south-eastern mainland Australia during winter and spring.
- Above average minimum temperatures across much of Australia, due to cloud trapping warmth in overnight.
- Extreme cold days are more likely across southeastern Australia, while extreme cold nights are less likely.
- Above average snowfall during winter and spring.
For more information on Weatherzone’s detailed seasonal outlooks, please contact us at apac.sales@dtn.com.