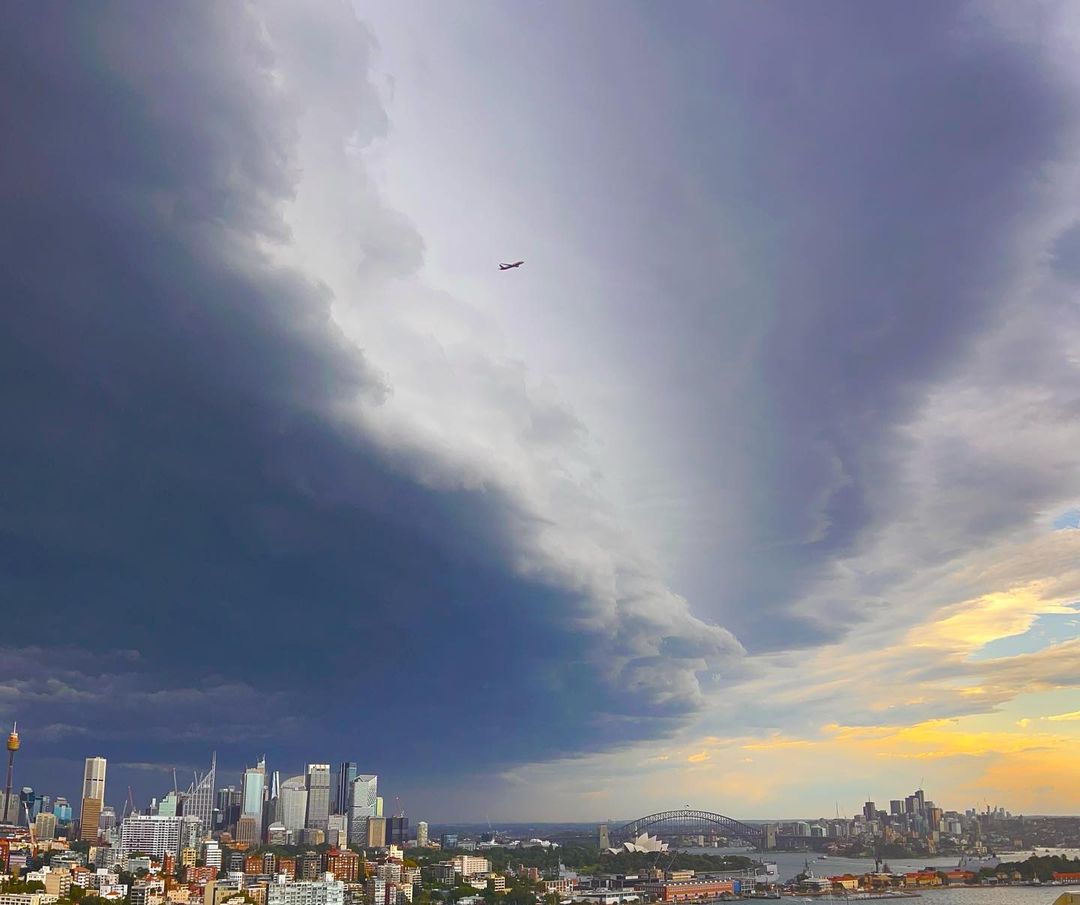
After a hot and humid Saturday, severe thunderstorms in the form of a squall line rolled through Sydney, bringing gusty winds, heavy rain and even some small hail.
Sydney’s western suburbs sweltered in temperatures mostly between 36°c and 38°c on Saturday afternoon. Sea breezes made the temperature a little more bearable closer to the coast, with tops of 30°c in the city, though the sea breeze did bring increased humidity, making it feel a few degrees warmer. Some relief was on the way though.
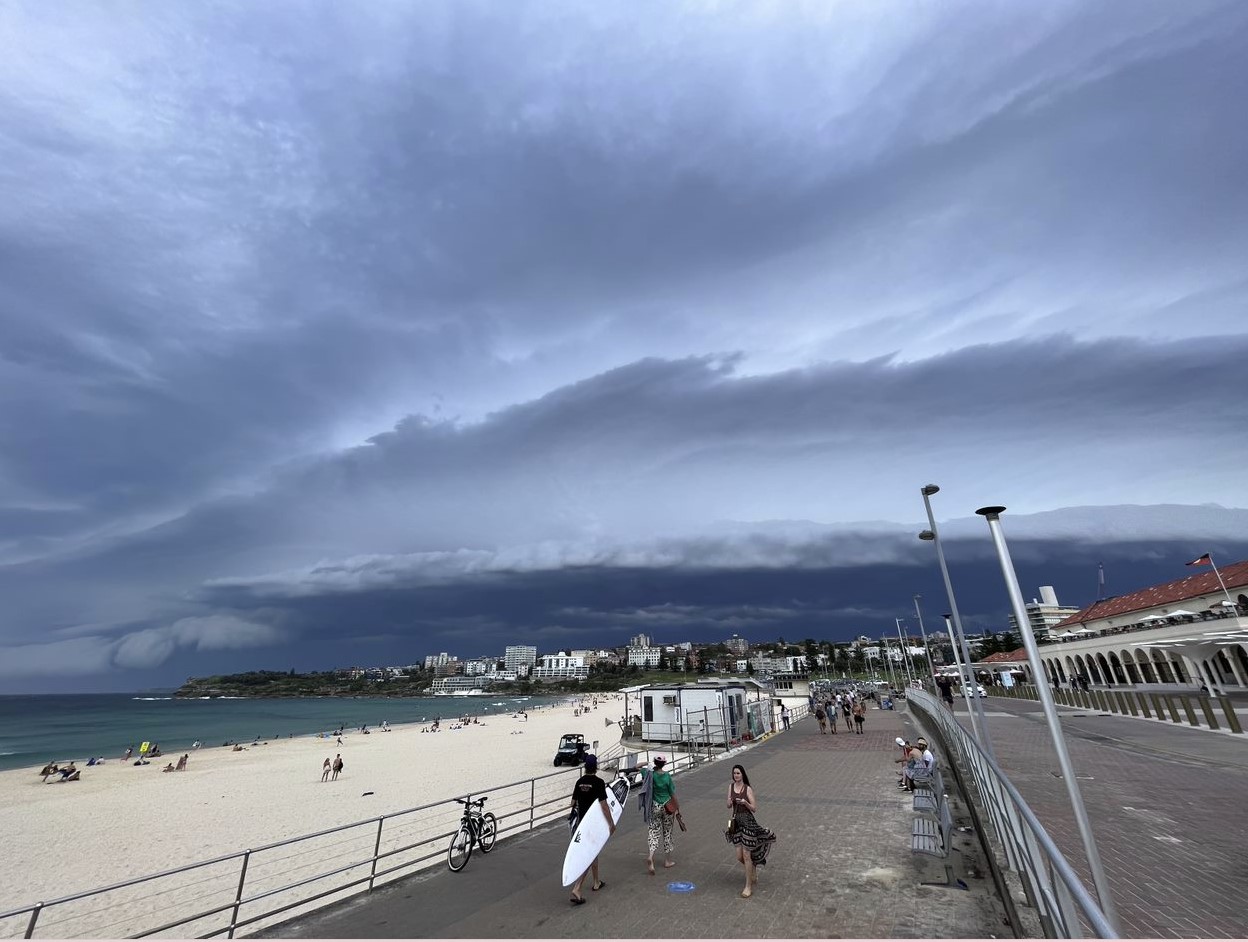

Image: A squall line approaches Bondi Beach. Photo by Tom Hough.
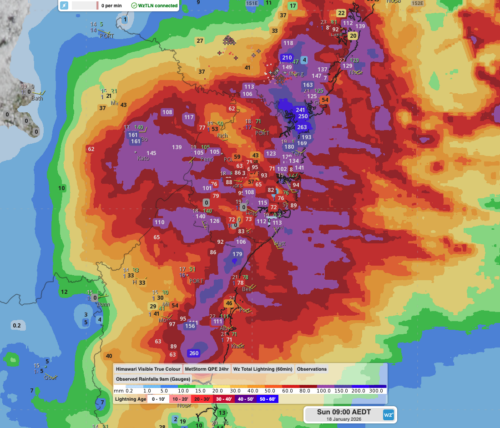
In the early afternoon, over the Southern Tablelands, storms began to spark to life. They grew and became more organised, becoming a squall line, as they marched northeast, heading for Sydney. The squall line swept through Sydney during the early evening, starting with the southwestern suburbs, before moving through the rest of the Harbour City. By the time the storm had passed, over 25,000 lighting strikes were recorded within 100km of Sydney.
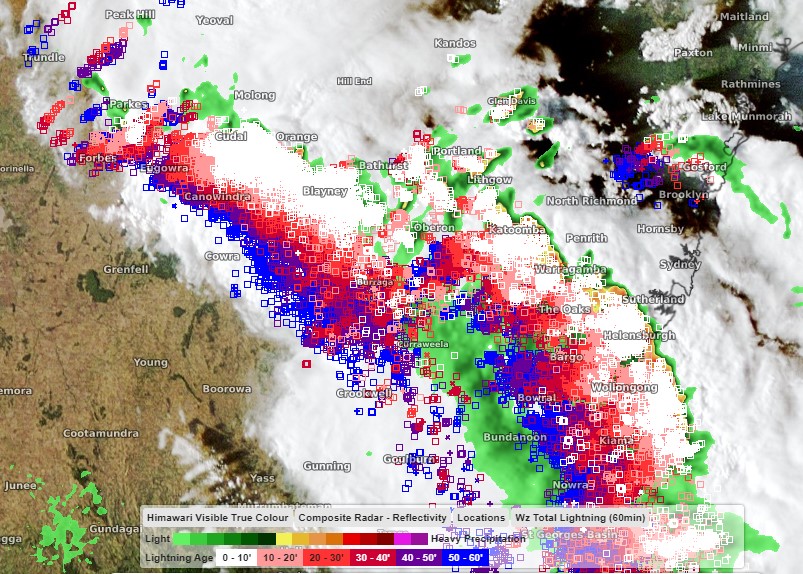
Image: Radar, satellite and lightning imagery showing a squall line closing in on Sydney.
The two key features of the storm were the gusty winds and the heavy rain. Port Botany recorded the highest wind gust in Sydney, reaching 106km/h. Elsewhere, Sydney Airport had a gust of 91km/h, Badgerys Creek 87km/h, Lucas Heights 85km/h and Holsworthy 83km/h.
The highest rainfall totals were mostly between 10-20mm, whilst that may not sound impressive, the rate at which it fell in some suburbs was. At Holsworthy, 11mm of rain was recorded in just ten minutes, with 8.4mm falling at Lucas Heights and 7.4mm at Bankstown, in the same time frame.
The storm also brought some welcome relief from the day’s heat. As the storm passed over Holsworthy, the temperature dropped over ten degrees in half an hour. The drop was less extreme in the city with a four-degree temperature drop.
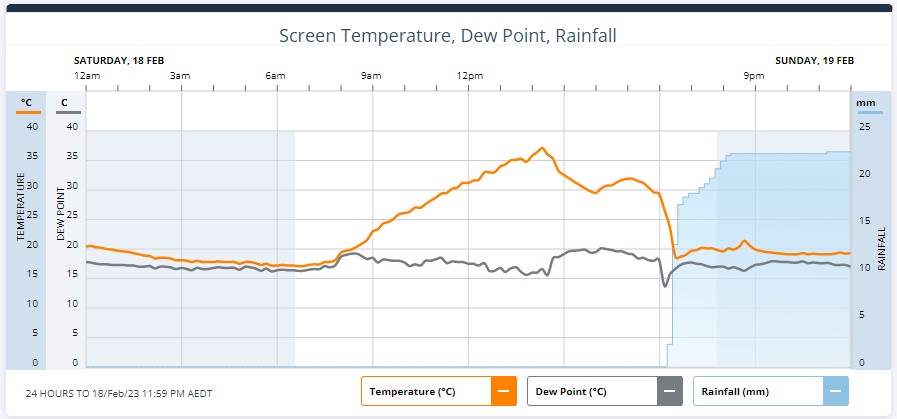
Image: Graph showing the temperature (orange line) drop at Holsworthy as the storm passed overhead.
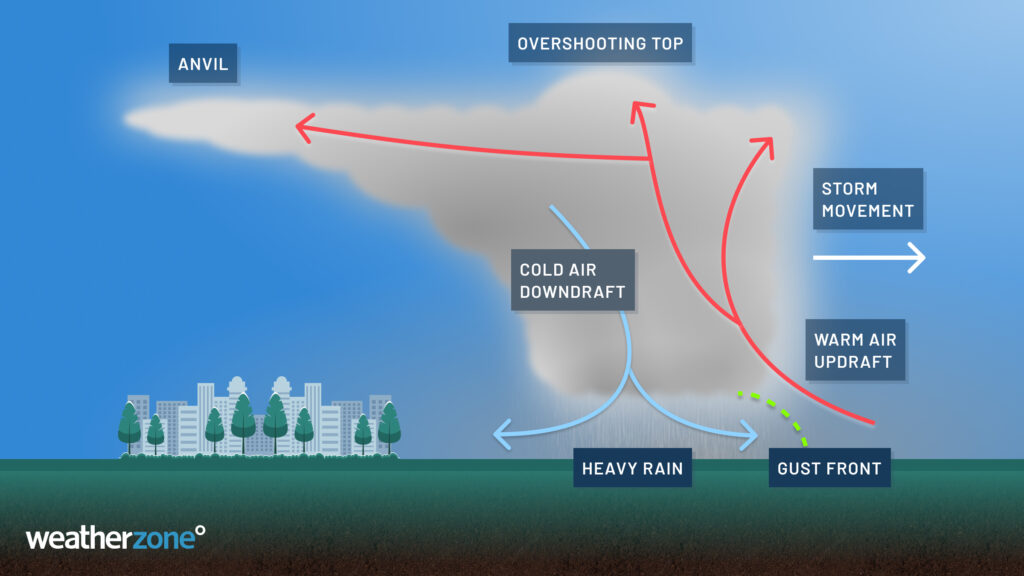
Saturday’s storm was a good example of what a squall line is and can do. You can read more about “What is a squall line” here.
Many industries can be greatly affected by squall line thunderstorms, including energy networks, mining and aviation. DTN APAC forecasts these thunderstorms ahead of time, and our meteorologists can provide special weather briefings if severe weather is expected for your business. To find out more, please email us at apac.sales@dtn.com.