New model data confirms that a La Niña-like pattern could persist in the coming months, increasing the likelihood of above-average rain in parts of Australia in winter and spring.
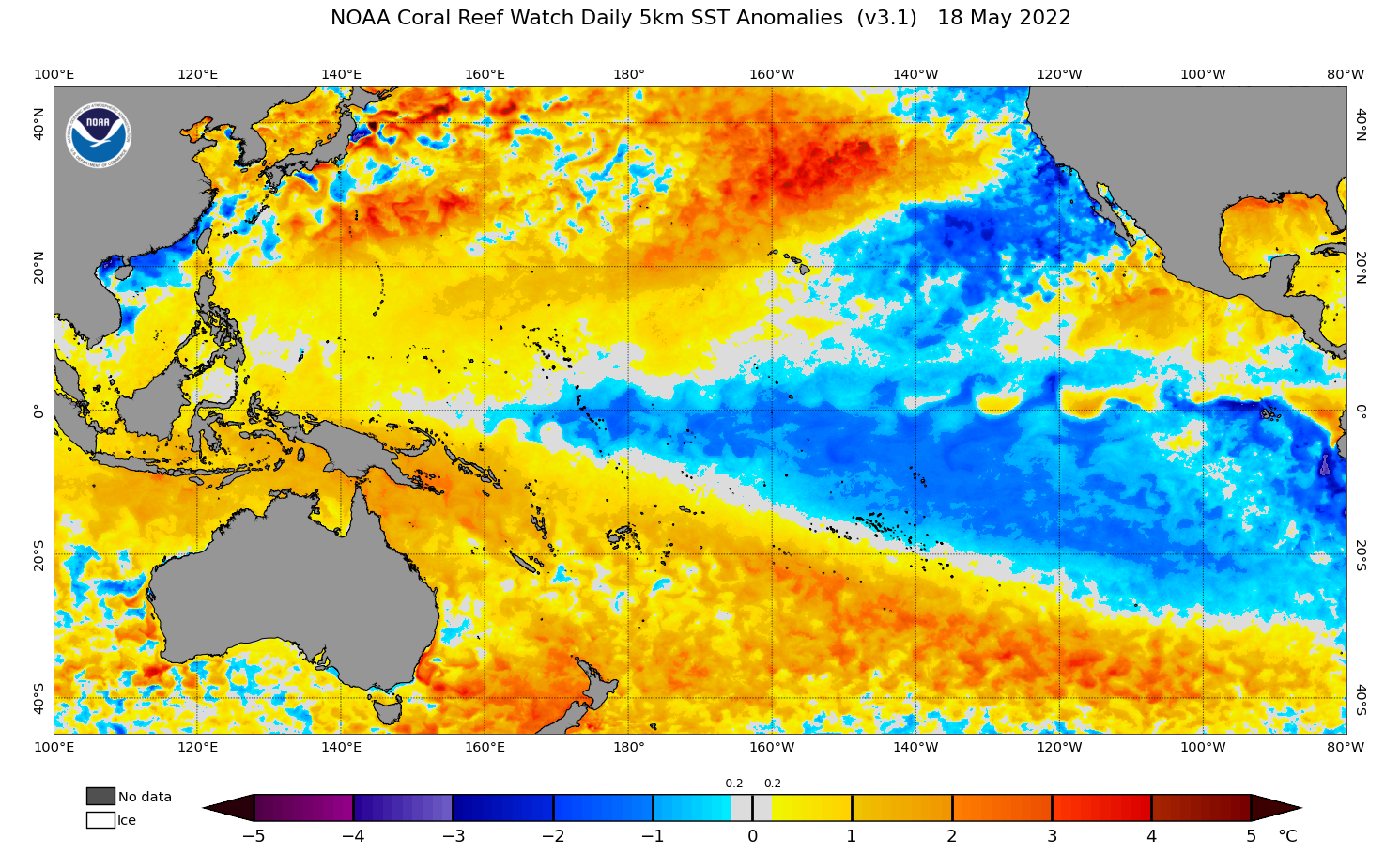
The Pacific Ocean has been in a distinctive La Niña pattern since late last year and during the last fortnight, this pattern has no signs of weakening.
Image: Current sea surface temperature anomalies in the Pacific Ocean, showing a distinctive La Niña pattern with cooler-than-average water in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean and warmer-than-average water in the western equatorial Pacific Ocean. Source: NOAA
The graph below shows the latest model-based prediction for La Niña (and its counterpart El Niño) from the Columbia University’s International Research Institute for Climate and Society (IRI) and the U.S. Climate Prediction Centre (CPC). This data was published on May 19, 2022.
Image: El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) forecast for the next 10 months, according to the U.S. CPC/IRI. The blue bars show the probability of La Niña occurring during each three-month period, with grey and red bars representing the probability of neutral and El Niño, respectively. Source: CPC/IRI
The graph shows that, according to the latest IRI/CPC model forecast, La Niña has a 62 percent chance of persisting through the southern hemisphere winter and a 58 percent chance of occurring in spring.
The continuation of a La Niña-like pattern in the coming months is also being predicted by most of the international forecast models that are analysed by the Bureau of Meteorology.
The first graph below shows that all models surveyed by the Bureau expect sea surface temperatures in the equatorial Pacific Ocean to be near or exceeding La Niña thresholds in late-winter. The second graph shows that by mid-spring, four out of seven models are in a La Niña state.
Image: Comparison of international seasonal forecast model’s predictions of central equatorial Pacific Ocean temperatures in August 2022 (top) and October 2022 (bottom). Source: Bureau of Meteorology
The Bureau of Meteorology’s outlooks currently only go out until October. However, the IRI/CPC graph near the top of this article shows that their modelling gives roughly equal weighting to La Niña and neutral (neither La Niña nor El Niño) conditions in the Pacific Ocean during the southern Hemisphere’s summer.
The main takeaway from these datasets are:
- La Niña or a La Niña-like pattern are predicted to linger through the middle of 2022, possibly encompassing both winter and spring in the Southern Hemisphere.
- This would increase the likelihood of above-average rain and below-average daytime temperatures over large areas of Australia during winter and spring, as shown in the map below.
- There is still some uncertainty between forecast models, especially beyond the Southern Hemisphere’s spring.
Image: Average winter-spring rainfall deciles from 12 La Niña years combined, indicating what the average rainfall footprint of La Niña looks like. Source: Bureau of Meteorology.
Image: Average winter-spring temperature deciles from 12 La Niña years combined, indicating cooler daytime temperatures across southern Australia. Source: Bureau of Meteorology.
The impacts of this ongoing La Niña are also likely to be enhanced by a developing negative Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) in the coming months.
A negative IOD increases the likelihood above-average rain and cooler-than-average daytime temperatures in Australia. A number of forecast models suggest that we could see a strong negative IOD this winter and spring. For more information on Weatherzone’s seasonal forecasts, please contact us at apac.sales@dtn.com.