The Bureau of Meteorology has today declared the end of the 2022 negative Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD), reducing the likelihood of above-average rain over large areas of Australia as we head into summer.
The IOD is an index that measures the difference in sea surface temperatures across the tropical Indian Ocean.
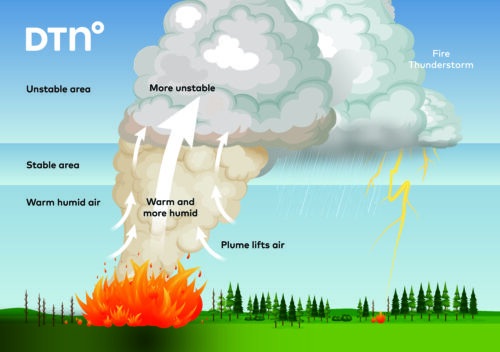
When the IOD is in a negative phase, unusually warm water sits on the eastern side of the tropical Indian Ocean, near Indonesia, while abnormally cold water lies on the western side of the Indian Ocean, near the Horn of Africa. Negative IOD patterns allow more moisture-laden air to flow towards Australia from the northwest, which usually enhances rainfall and promotes flooding.
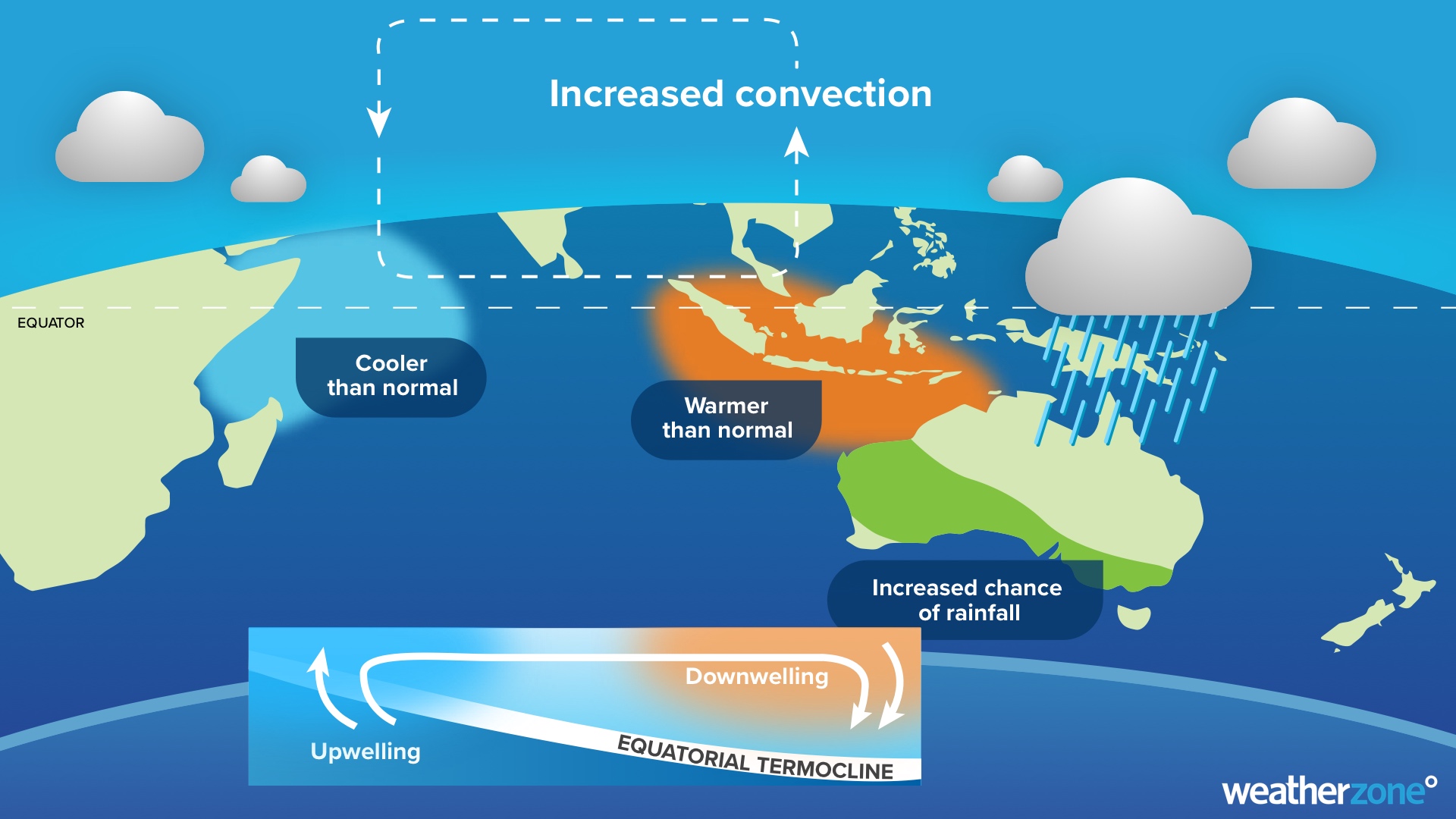
Image: Typical negative IOD pattern and impacts.
This year, a negative IOD was declared by the Bureau of Meteorology at the beginning of August. In the months that followed, Australia endured its 5th wettest September, wettest October, 10th wettest November and second wettest spring on record.
This recent run of exceptionally wet months inundated the landscape and caused major flooding across several states. The negative IOD in 2022 also helped Sydney register its wettest year on record.
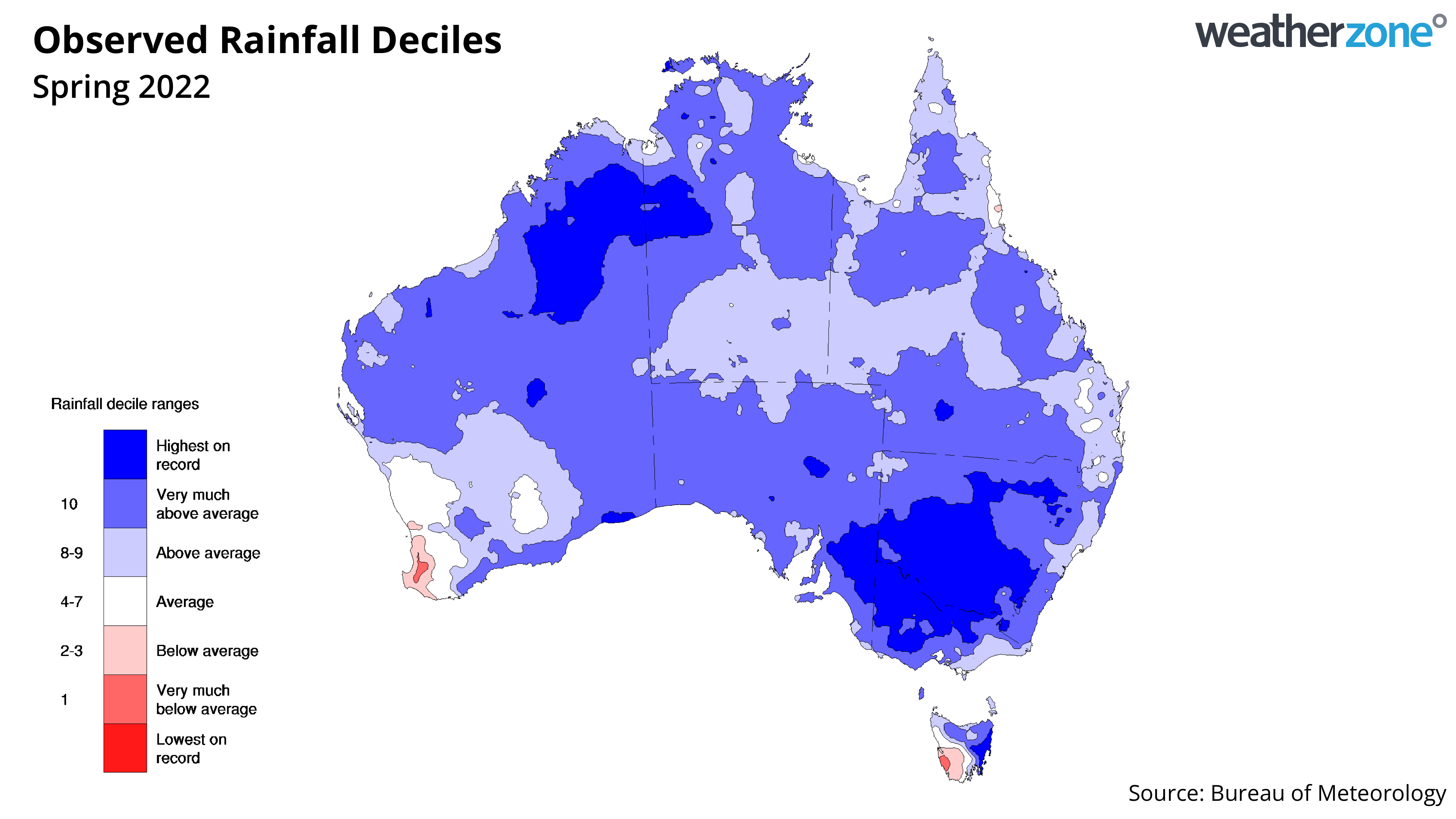
Image: Spring 2022 rainfall deciles.
There are clear signs that the negative IOD has now come to an end. The IOD index rose back above the negative IOD threshold of -0.4ºC at the beginning of November. The index has remained in the neutral range (-0.4ºC to +0.4ºC) since then, with the latest weekly value reaching -0.16ºC in the week ending on December 4.
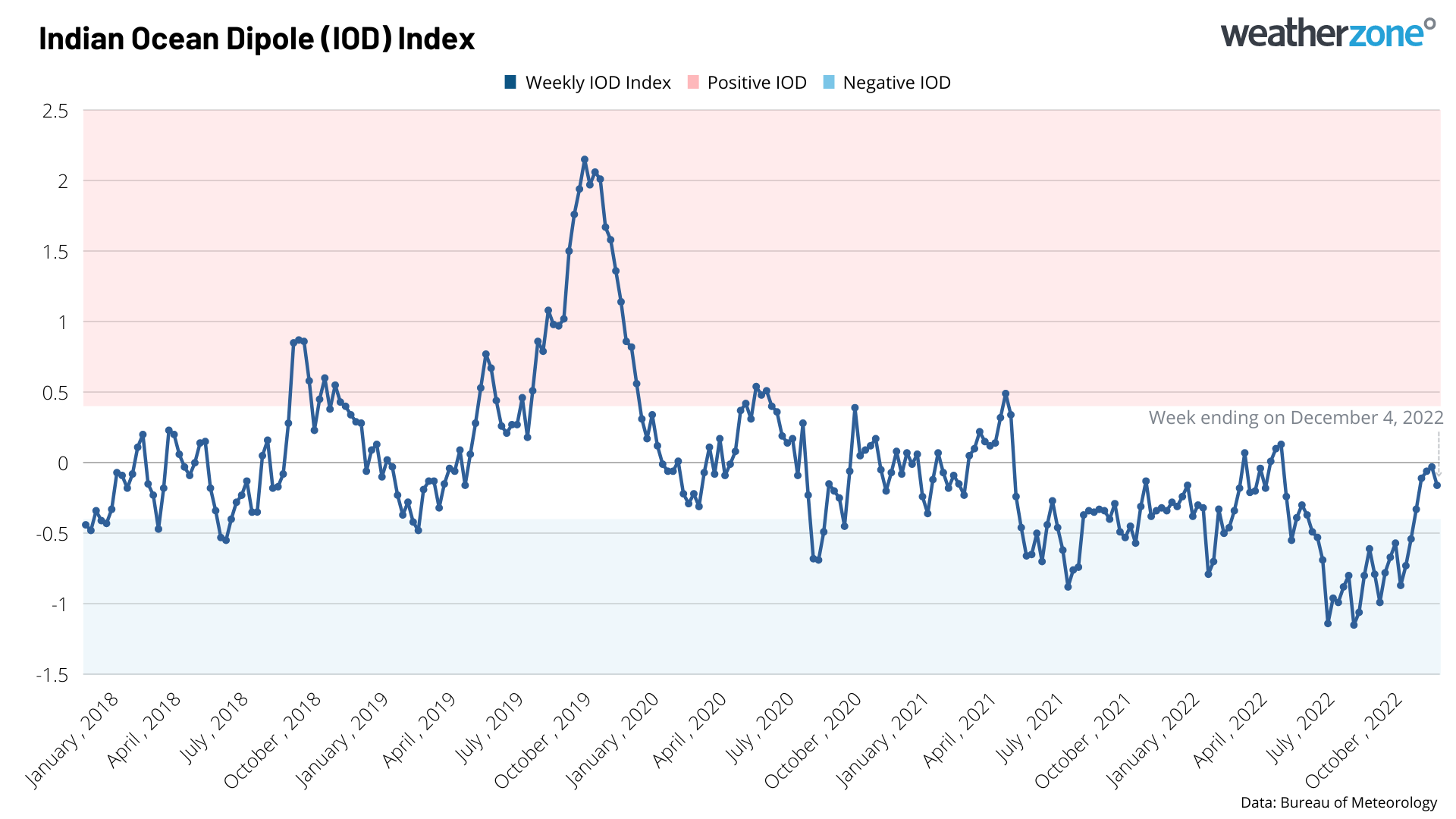
Image: Weekly Indian Ocean Dipole Index (IOD) values over the past five years.
In response to this five-week string of neutral values, the Bureau declared the end of the 2022 negative IOD on Tuesday, December 4.
In the absence of the negative IOD, rainfall over Australia will now become more strongly influenced by sea surface temperatures near Australian and over the Pacific Ocean.
The image below shows that large areas of western, central and southern Australia are expected to see near or below average rainfall and above average maximum temperatures this summer. However, the ongoing influence of La Nina and warm local seas should help boost rainfall and suppress daytime heat in parts of eastern Australia in the coming months.
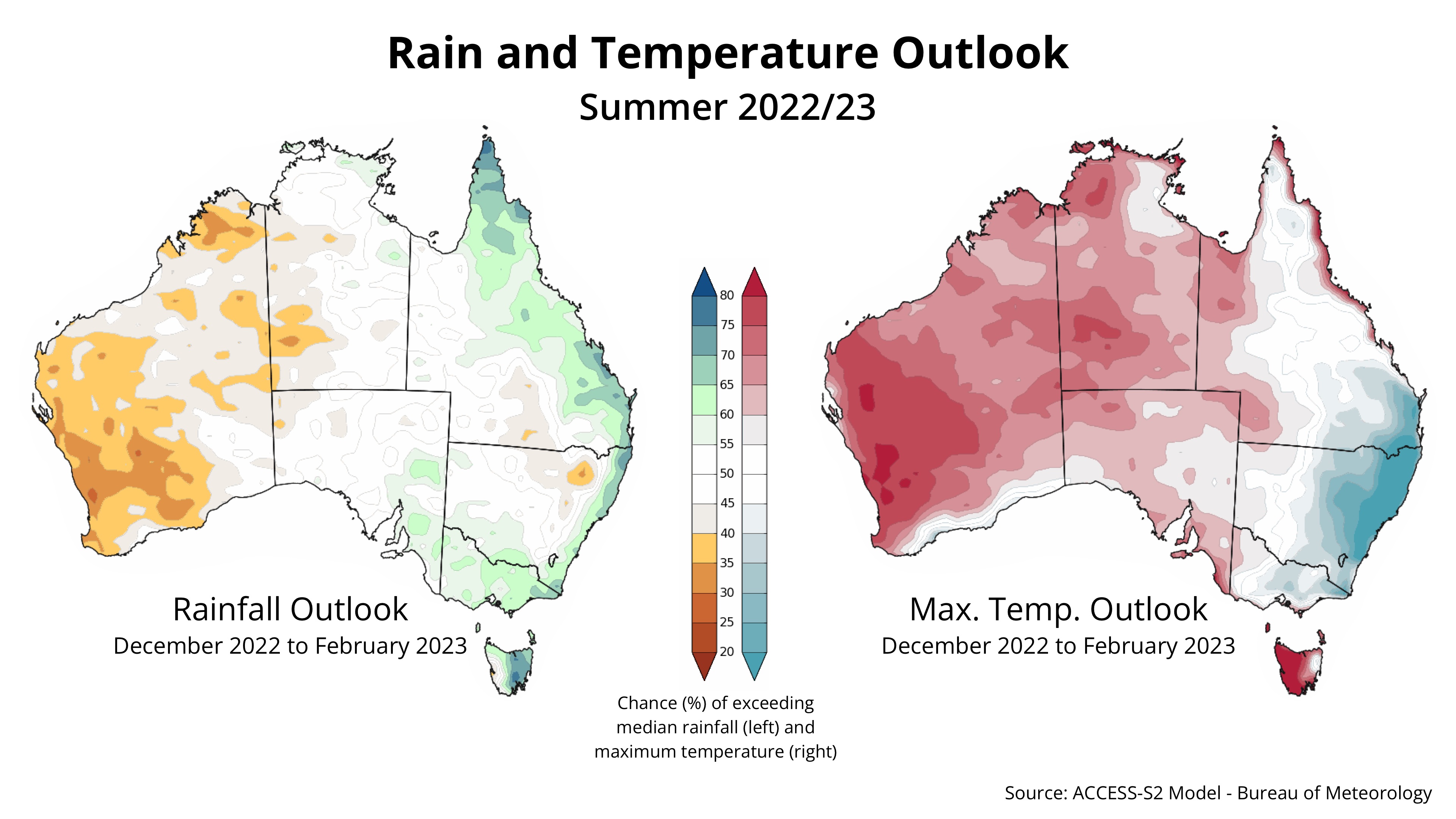
Image: Australian rainfall and maximum temperature outlook for summer 2022/23, based on the ACCESS-S model.