After three successive La Niñas, there are strong signs that the latest La Niña is quickly waning and will release its grip and move towards neutral in its effect on Australia in the second half of summer into autumn, as the previous two did.
This means we can expect an end to the relentlessly wet weather which has lashed large parts of Australia in recent summers, and for much of 2022 – with a return to drier, potentially warmer conditions as we move through summer.
How do we know this? The chart below tells you most of what you need to know.
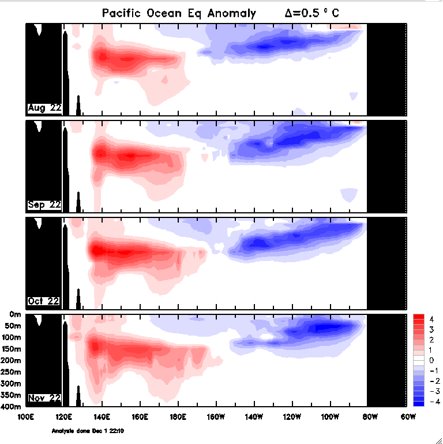
- The chart shows an ocean pattern called the Kelvin wave – which moves across the Pacific underneath the surface of the ocean – transporting the warmer-than-usual water that we’ve had in Australian waters back into the central Pacific.
- At the same time, this is causing the colder waters in the eastern Pacific to retreat, slowly shutting down the cycle.
In simple terms, as those red blobs move west (or to the right of the chart), the effects of La Niña become less pronounced.
Why does warmer water moving away from our region signal the end of La Niña?
Because warm-than-usual water near Australia is La Niña’s fuel.
If you go back to the La Niña explainer piece which we wrote in September 2022, we told you that La Niña occurs when:
- The temperature contrast that develops across the equatorial Pacific Ocean supports stronger trade winds blowing from east to west across surface of the Pacific.
- These enhanced trade winds cause warmer-than-average water to pile up on the western side of the equatorial Pacific Ocean and cooler-than-average water to form in the central and western equatorial Pacific.
- The pools of abnormally warm and cool water help air rise over the western Pacific Ocean and sink on the eastern side of the Pacific basin. This rising and sinking air causes enhanced convection and cloudiness near Australia. Or in other words, a much stronger likelihood of rain.
Here’s the super quick version if your concentration is waning (like La Niña) right now due to the common affliction known as end-of-year-itis:
The ingredients for La Niña are vanishing, and quite quickly.
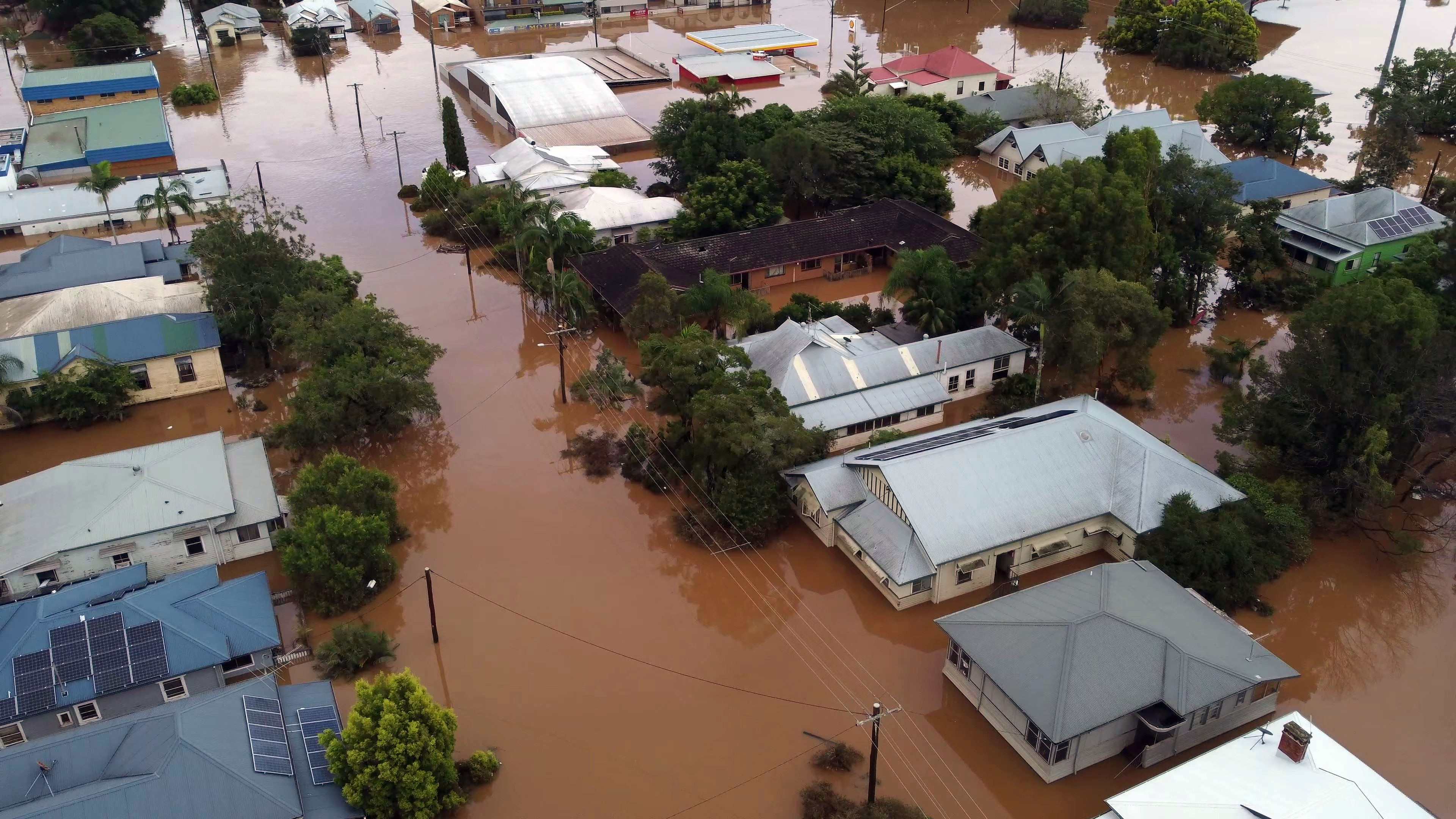

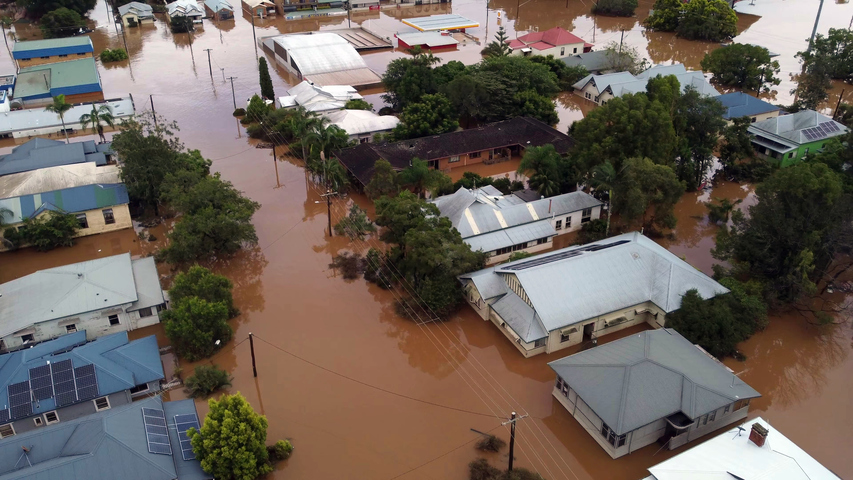
Image: Hopefully we’ll see fewer scenes like this in the near future. Source: iStock.
Arguably we have already seen a glimpse of La Niña’s weakening influence over the last week or so in Australia, with a period of dryish weather in most parts of the country south of the tropics.
As La Niña continues to weaken, the rain taps will of course not totally turn off. The weather will still deliver its daily and weekly mix of conditions irrespective of underlying climate drivers which point towards broader wet or dry trends.
But overall, a drying trend realtive to average is now looking likely across much of the country. Whether we see the opposite of La Niña – El Niño – with its signature hot, dry summers in the near future is not yet clear.