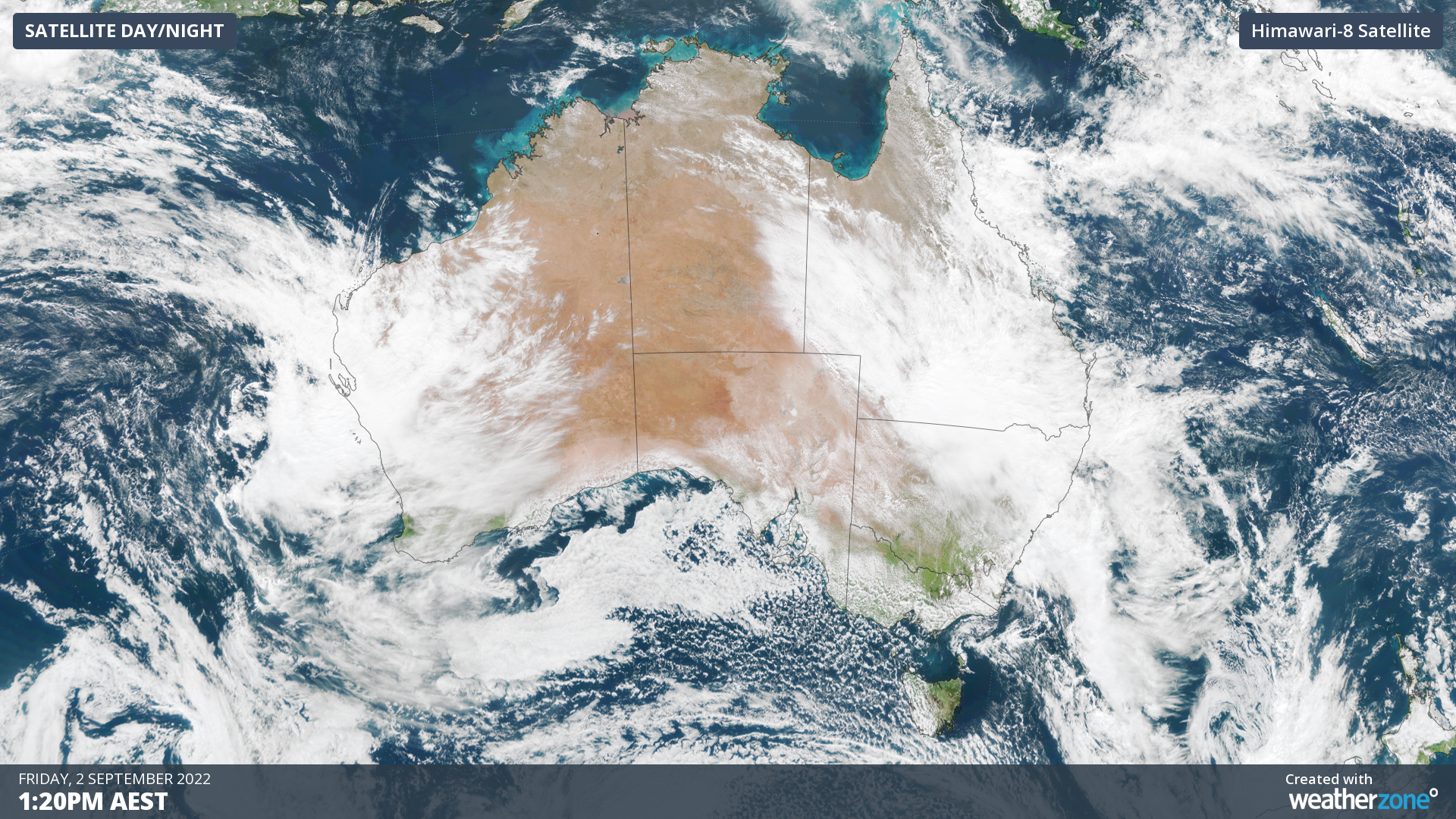
More than 100 mm of rain could fall over parts of northeast NSW during the next three days as a mass of tropical moisture and cloud spreads rain and dampens solar across a large swathe of eastern Australia.
The animation below shows three hours’ worth of satellite images from Friday morning, capturing a large and thick northwest cloudband passing over eastern Australia.
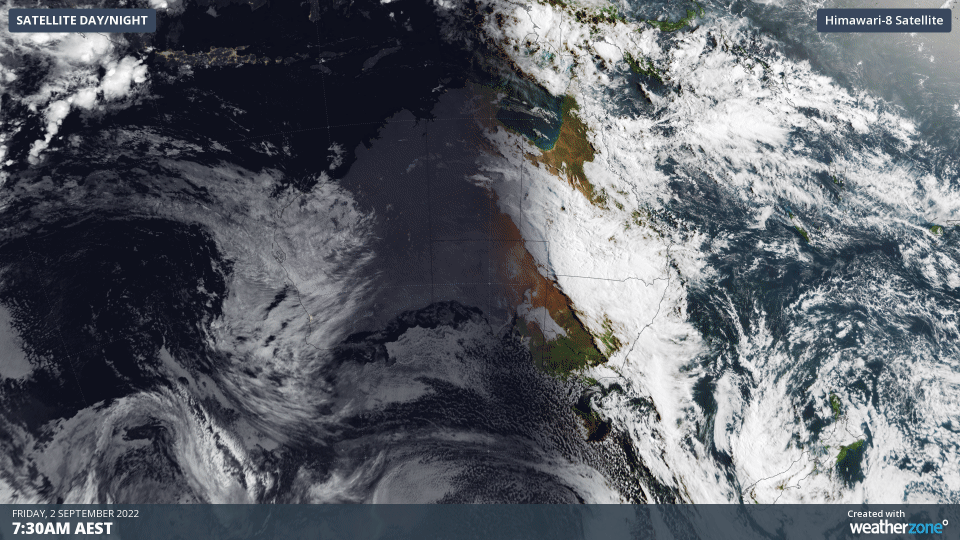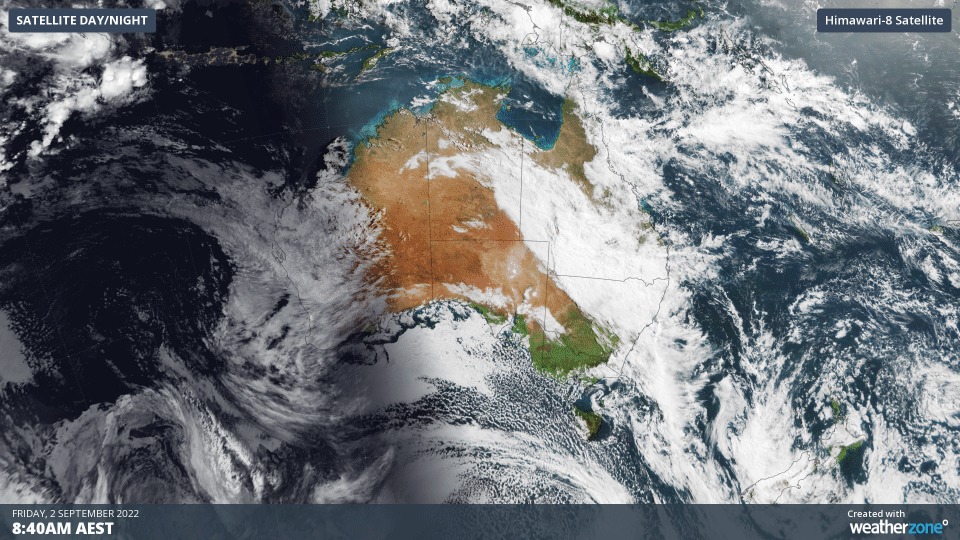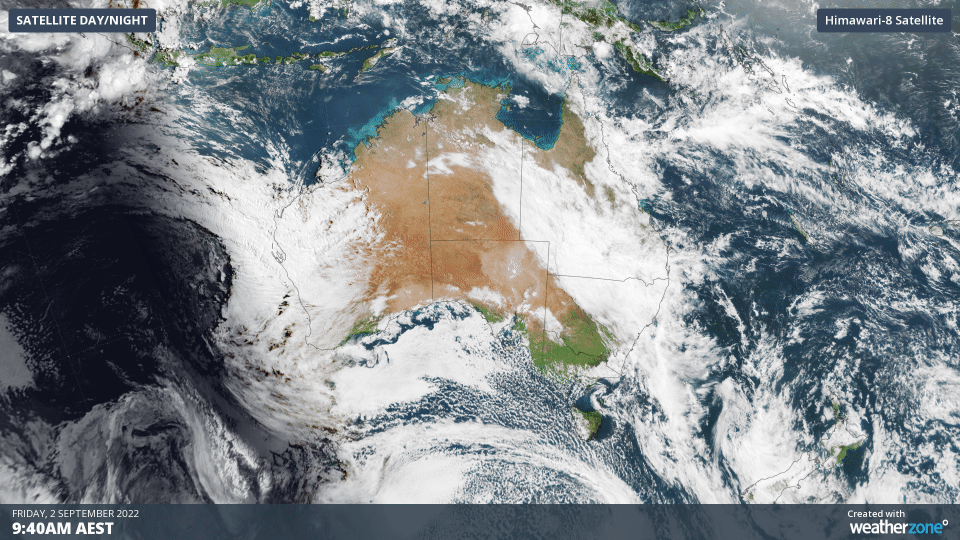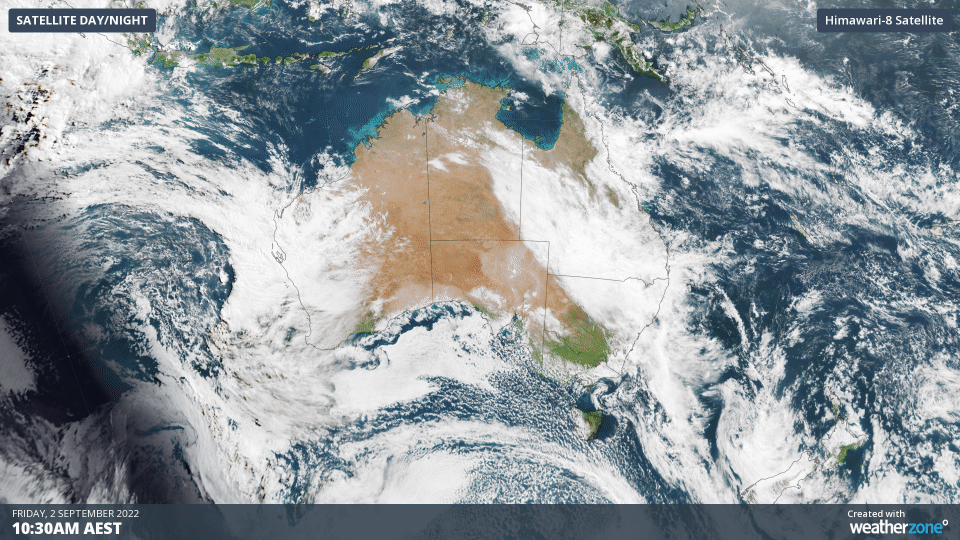
Over the past two days, this cloudband has produced more than two months’ rain in parts of southwest QLD.
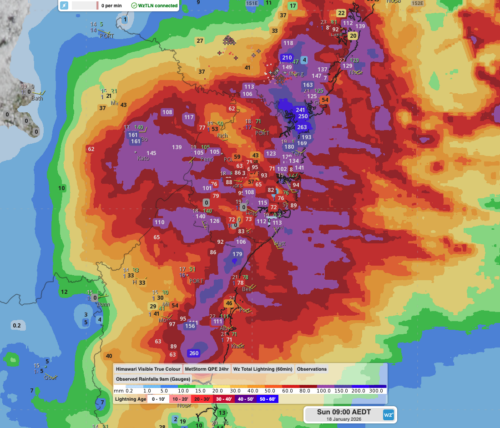
Over the next three days, the cloudband will continue to produce rain over a broad area of southern QLD and northern NSW. The map below shows how much rain one computer model is predicting between Friday and Sunday from this cloudband.
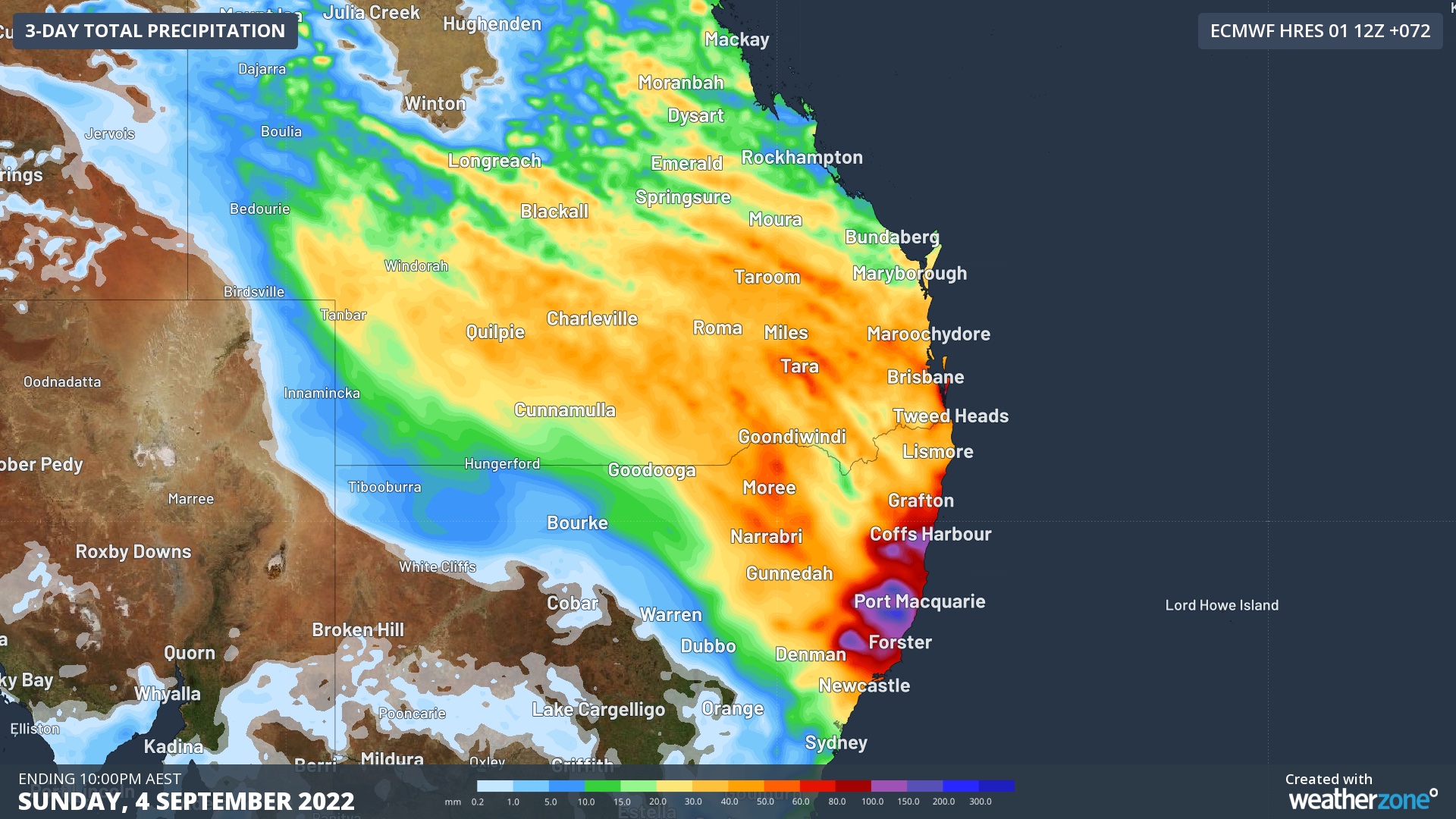
Image: Forecast accumulated rain during the 72 hours ending at 10pm AEST on Sunday, September 2.
As the map above shows, widespread falls of 30 to 50 mm are likely over southern QLD and northeast NSW between now and Sunday. The heaviest rain is expected to fall along the Mid North Coast and adjacent ranges in NSW, where isolated totals in excess of 150 mm are possible. This may cause riverine flooding in some areas, with a flood watch issued on Firday afternoon for the the Orara, Bellinger and Hastings Rivers.
The exact location and intensity of the heaviest rain will depend on the location of a low pressure system that is expected to develop off Australia’s east coast on Saturday. As this dynamic low pressure system is difficult to predict, rainfall forecasts may jump around a bit in the next 24 to 48 hours.
This low pressure system could also produce damaging winds and hazardous surf along parts of the NSW coast on the weekend.
The thick cloud encompassing eastern Australia is also expected to reduce solar output significantly for several days, particularly across QLD.
Weatherzone, in partnership with Solcast, provides solar power forecasting and solar irradiance data, for both large-scale solar farms and small-scale PV systems, plus their grid or regional aggregates. For more information, please contact us at apac.sales@dtn.com.