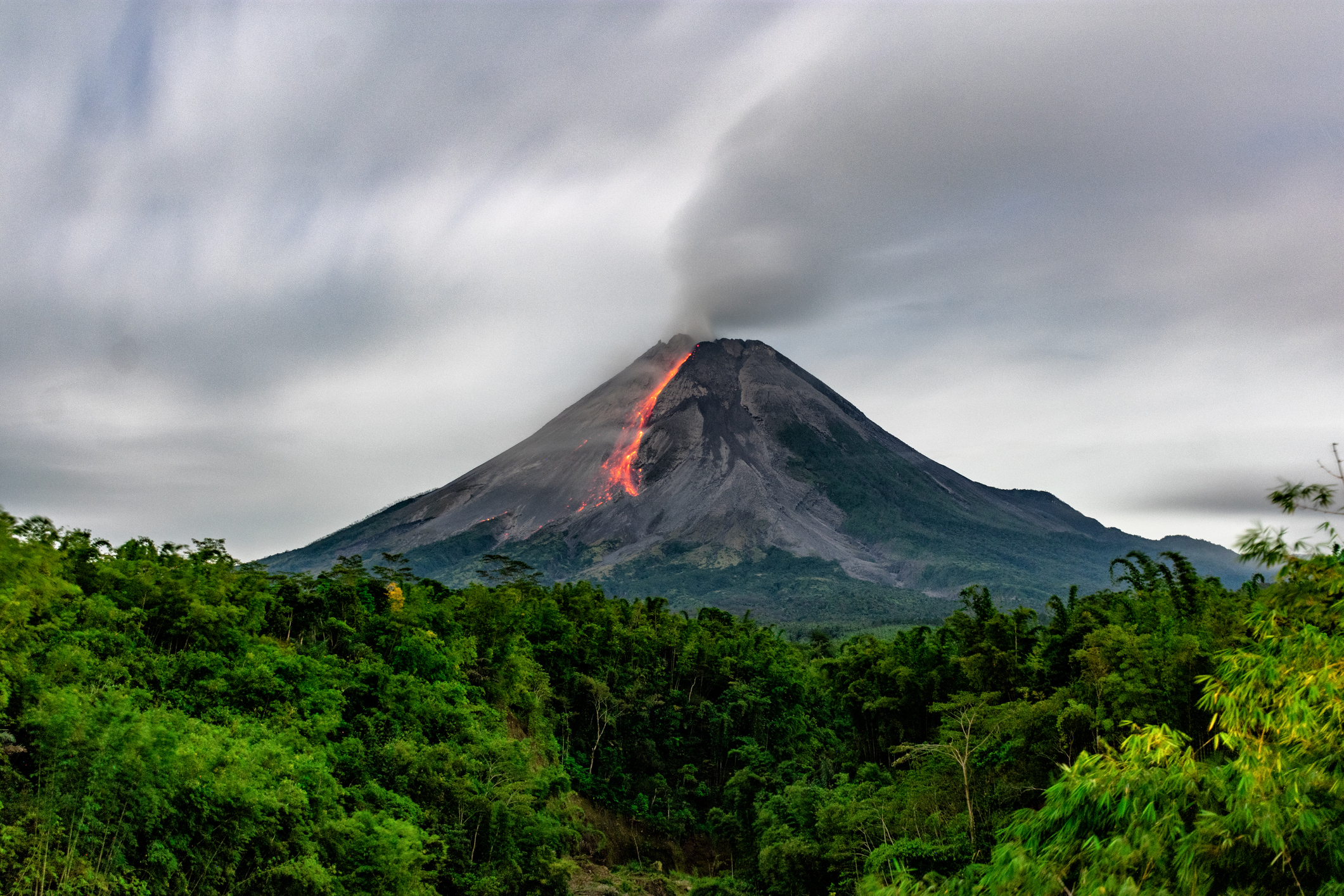
On Saturday, Indonesia’s most active volcano, Mount Merapi, erupted, sending huge plumes of ash into the sky. It serves as a large-scale reminder of how ash and dust from explosions, including in mining and demolition, can travel and spread.
Mount Merapi erupted at 5am UTC (1pm WST) on Saturday afternoon. Most notable was a fast-moving pyroclastic flow full of superheated lava, ash and rock that spewed down the volcano’s southwestern face.
1/3
Woahhh!
Today: Massive eruption at Merapi #volcano, #Java, #Indonesia. Pyroclastic flow of hot rock fragments, volcanic gases, and air descended on southeastern flank. Reached 7km from summit, close to populated areas. No reported casualties yet. #Merapi pic.twitter.com/sXM7vZmRZO
— Volcaholic (@CarolynnePries1) March 11, 2023
The ash cloud could be seen from space, though was difficult to visually distinguish from thunderstorms developing nearby. Here is an enhanced feed from the Himawari-9 satellite that highlights fine particles in the air. In this case, the ash appears as bright pink, compared to the surrounding storm clouds in yellow.
The pink cloud can be seen initially shooting off to the southwest of the volcano as the pyroclastic flow ran down its side and gave it momentum. As the ash cloud grew and time passed, the cloud then starts to drift to the northwest, driven by the southeasterly winds over the region.
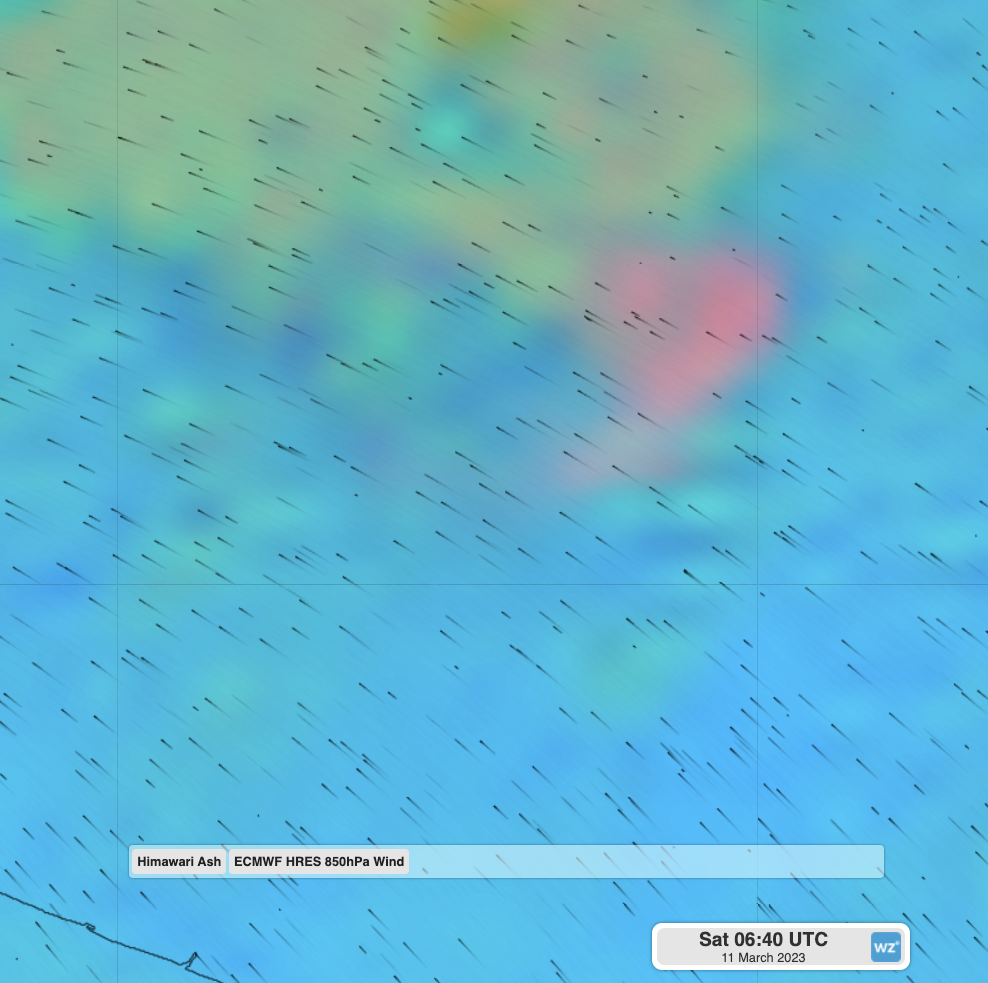
Image: Himawari-9 enhanced satellite and black wind streamlines showing the winds at about 1km elevation spreading the ash cloud to the northwest.
While a volcanic eruption is obviously a very large explosion, the behaviour of dust, ash, smoke and fine particles are the same on smaller spatial scales. When explosions are used for mining or demolition, particles are sent into the air that can cause harmful effects to workers or nearby communities near to the site.
DTN APAC’ Blast Dispersion uses weather models and your explosive input parameters to generate a simulation of how fine particles and nitrous oxides will travel after a blast. By allowing you to select a range of dates and times, it allows you to identify when to detonate to minimise the effect of a blast to your personnel and local community.
Video: A sample blast dispersion showing the concentration of PM10 particles
For more information on Blast Dispersion, please visit our website or email us at apac.sales@dtn.com.