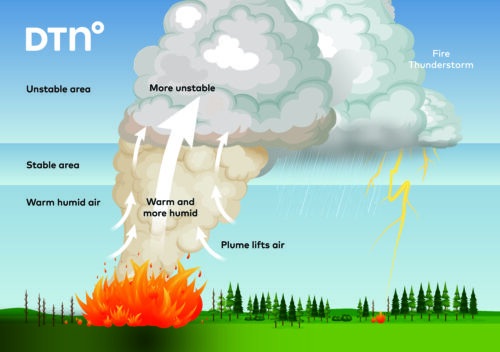
Tasmania’s impressive renewable energy achievements are facing challenges as low rainfall significantly reduces hydropower.
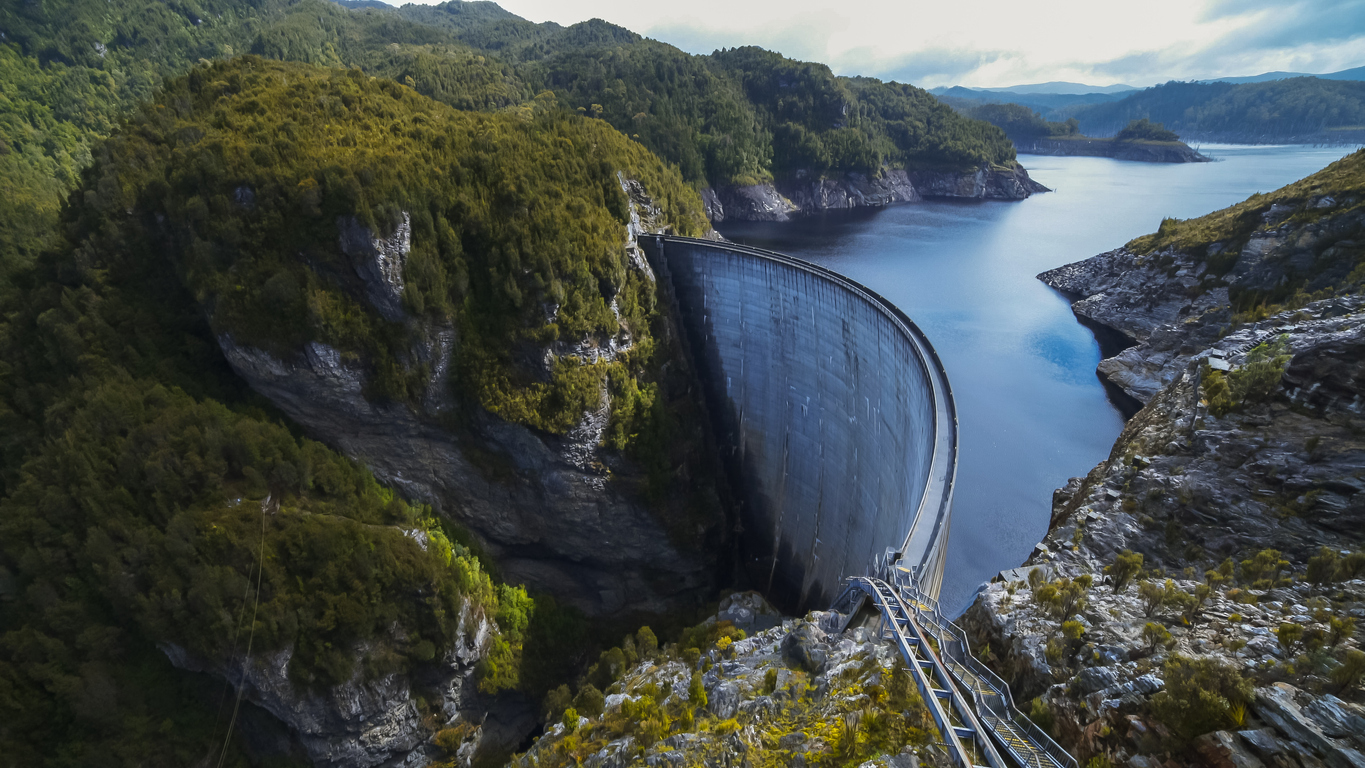
Hydro Tasmania is Australia’s largest generator of renewable energy, building 54 major dams, 30 hydropower stations and hybrid power stations.
Their hydropower station was built more than a century ago, with construction continuing into the 1990s.
The stations are in six high-rainfall catchments formed by natural river systems, which the power stations and water storages link together.

Image: Power stations by location. Source: Hydro Tasmania
During the first nine months of this year, these stations contributed 79% renewable energy to the electricity grid, an all-time low for the state. While during 2009, 2013, 2014, 2018, 2020 and 2021 the state was powered by 100% renewable energy.
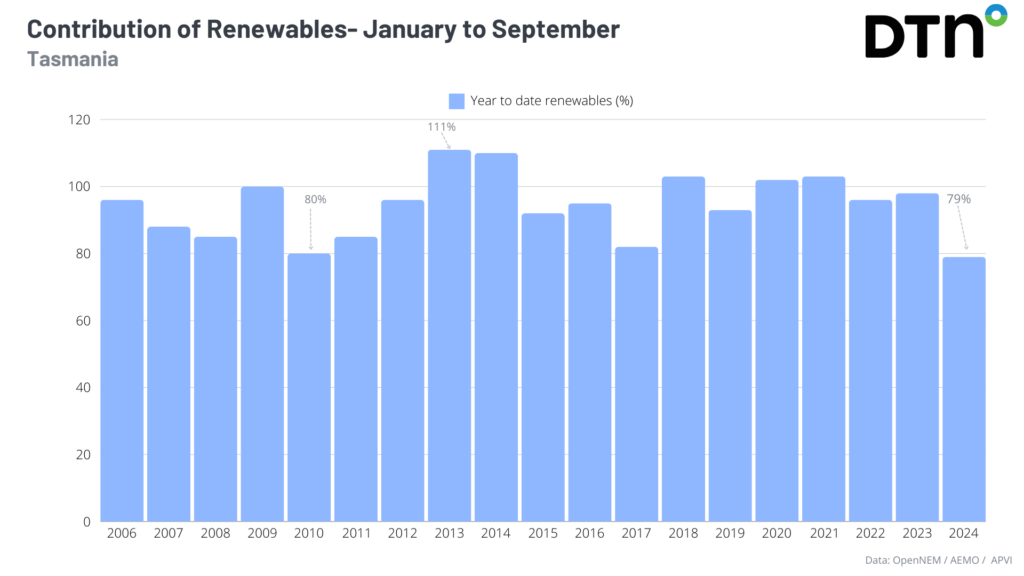
You can see in the graph below that most of the renewable contribution came from hydropower, with wind power contribution increasing from 2013 after Mussleroe Wind Farm was installed. Solar power has steadily grown in Tasmania over the last decade and wind power peaked last year.
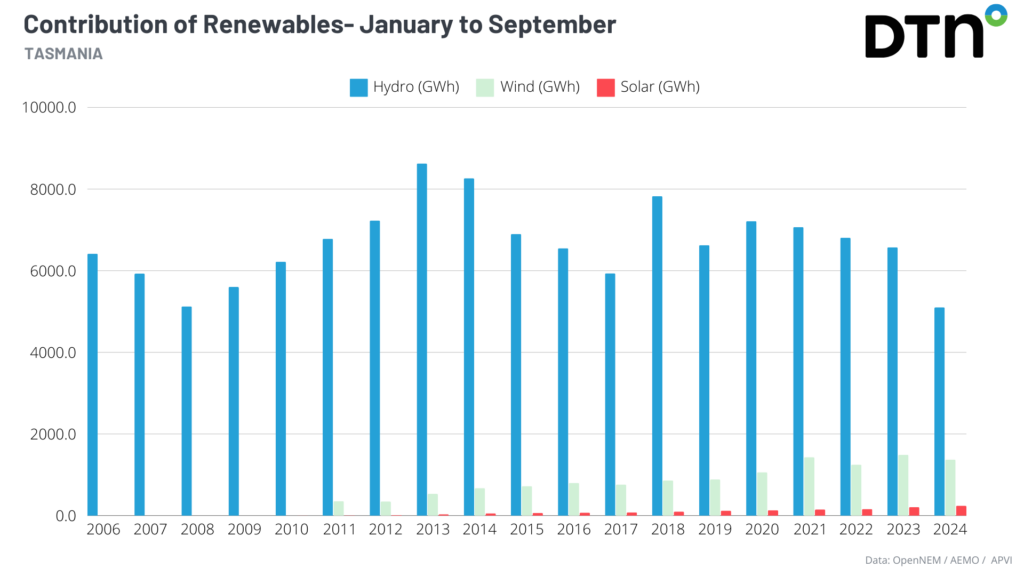
The outstanding hydropower years were of course linked to above average rainfall years for Tasmania, however installed hydropower capacity certainly played a part.
The lowest contribution to hydropower was seen in the first nine months of this year, with storage levels only at 48% on Monday, August 28.
This was caused by very much below average rainfall in the states west during the first half this year, with parts of the northwest recording the driest 6 months on record.
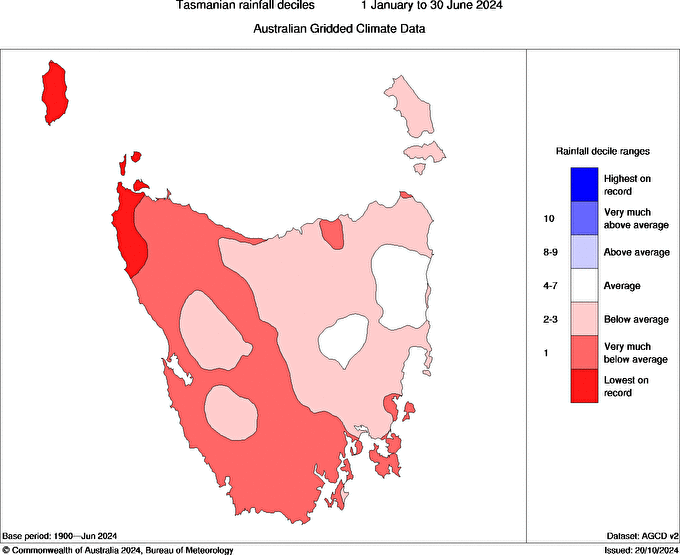
Image: 6-month rainfall deciles between 1 January and 30 June 2024. Source: BOM
The dry conditions were caused by high pressure sitting across southern Australia during summer and autumn which forced cold fronts and associated rain bands south of Tasmania.
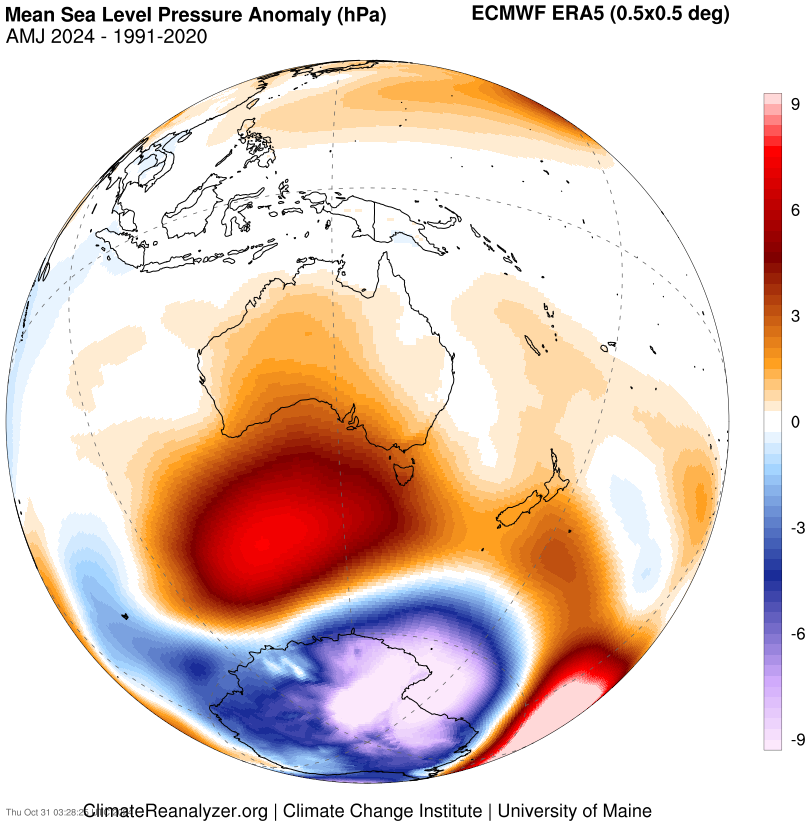
Image: Mean Sea Level Pressure Anomaly (hPa) showing high pressure (red) to the south of Australia. Source: ClimateReanlyzer.
This pattern was interrupted by a Sudden Stratospheric Warming event which promoted negative SAM causing frequent cold fronts to move over the state between mid-July and September.
The series of cold fronts brought much needed rainfall to the state, albeit at times the weather turned severe with damaging winds and heavy rainfall.
Looking ahead, the SAM is expected to tend positive from mid to late November into summer which could reduce the frequency of cold fronts passing over the state.
This could lead to drier conditions on the west coast, while the east could see wetter conditions with moisture-laden easterlies coming off warm oceans.
Meanwhile, fewer cold fronts most likely will reduce wind production across much of the state.
Using Opticast’s nowcasting and forecasting capabilities, you will have long-term outlook covering rainfall and extreme heat events out to 12 months. This can significantly improve your planning as you integrate the data with site-specific hydrological parameters.
With renewables making up more of Australia’s energy mix every year, we want to support your business to make informed critical decisions and improve your overall generation and safety. Please visit our website or email us at apac.sales@dtn.com.
Thumbnail image: crbellette