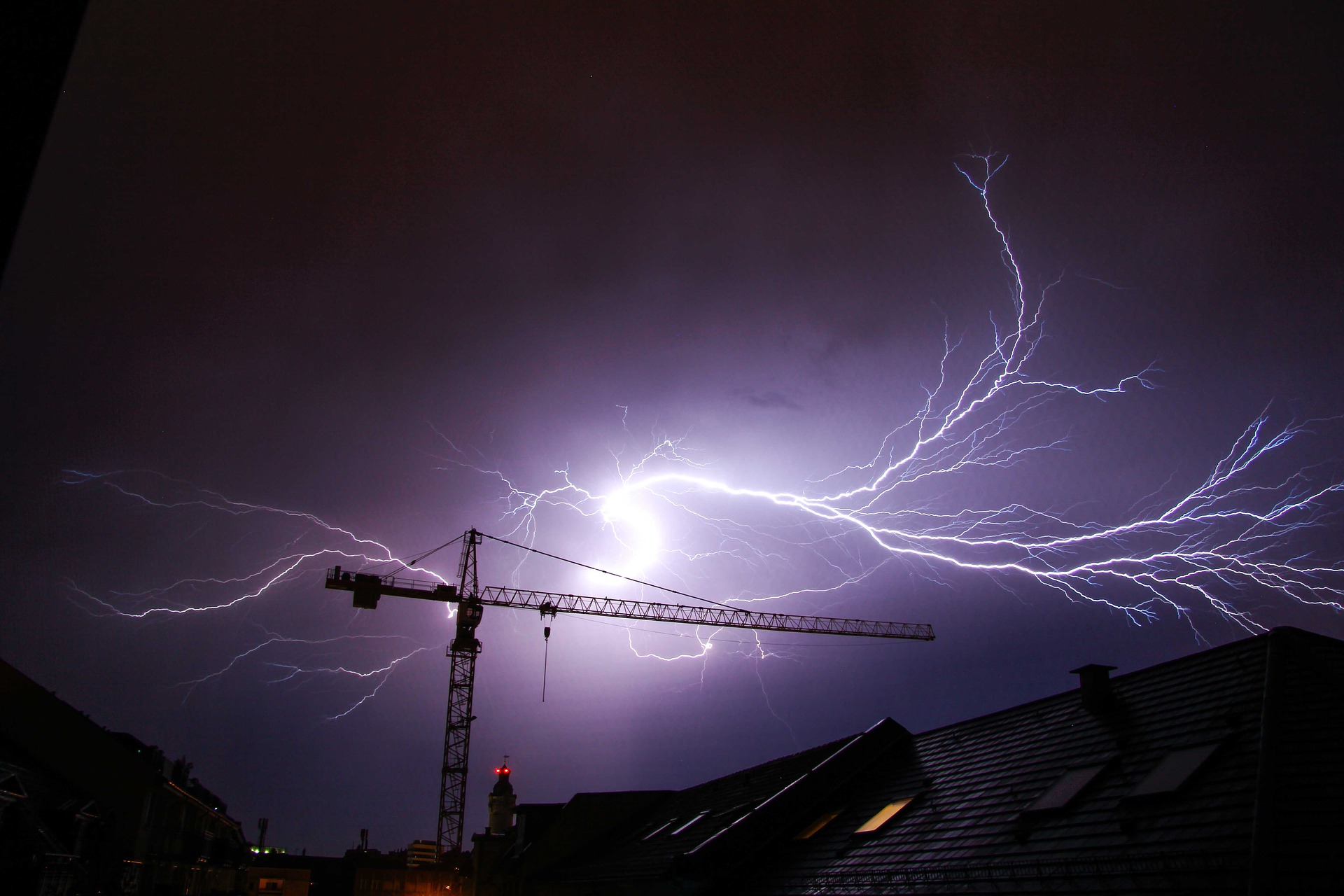
While lightning is a striking display, it is an extremely dangerous weather phenomenon. But what is lightning and how does it form?
Lightning is an electrical discharge that can occur within a cloud, between clouds, and between the cloud and the ground.
Lightning is also extremely hot. It can heat the air around it to a temperature of approximately 30 000 °C, which is hotter than the surface of the sun. This rapid heating makes the air expand rapidly, producing a shock wave that causes the loud sound known as thunder.
What causes lightning?
Thunderstorms contain millions of small ice crystals and super cooled water droplets which move up and down in currents of air within the storm. These currents of air are known as updraughts and downdraughts.
As the water droplets and ice crystals travel in the updraught and downdraught, they bump and crash into each other, becoming larger.
This process causes a positive charge to develop at the top of the cloud, while a negative charge forms at the bottom (figure 1).
Figure 1: Positive charge at the top of a cumulonimbus cloud and a negative charge at the bottom.
You may have heard the term, ‘opposites attract’ and this is certainly the case with lightning.
Lightning occurs most often from cloud to cloud, between two areas of opposing charges. Less frequently, lightning also occurs between clouds and the ground as either negative or positive lightning.
Negative lightning occurs directly beneath the storm, between the bottom of the cloud which is negatively charged, and the ground, which is more positively charged.
Lightning can also occur between the top of the cloud (positive charge) and a negatively charged area of the ground, sometimes a long way from the storm itself (figure 1). This is known as positive lightning, which can be very dangerous and can strike up to 40km away from the parent storm. These clear-air strikes are sometimes called a ‘bolt from the blue’.
Positive lightning carries millions of volts of charge making them more dangerous than negative lightning strikes, which are typically weaker in charge. However, positive lightning is rare, with around 90 to 95 percent of strikes globally being negative lightning.
Because lightning looks for the easiest path to the opposite charge, tall objects such as towers and trees are often in the firing line. This is why it’s a good idea not to stand under a tree or hold an umbrella during a thunderstorm, and seek shelter indoors if you can.
So next time year hear thunder, it means that lightning is nearby and could strike at any time.
Weatherzone’s Total Lightning Network is driven by the Earth Networks Total Lightning Network®. This is the most reliable and precise lightning detection network in the world, so you can make better decisions, protect property, minimize downtime, and safeguard lives when and where it matters most.
For more information on our lightning network, thunderstorm forecasting and Dangerous Thunderstorm Alerts (DTA’s) contact us at apac.sales@dtn.com.