Blustering winds have lashed southeastern Australia over the last few days, but it’s more than just a cold front adding to the wind strength.
Over the weekend, a strong cold front crossed through the south, delivering gusty winds and alpine snow. Some of the strongest winds recorded have been:
- 122km/h Hogan Island (Vic)
- 111km/h Mount Buller (Vic)
- 109km/h Neptune Island (SA)
And while these winds gusts are strong, something more interesting has happened in NSW. The strongest wind gusts recorded in the state over the last 24 hours are:
- 100km/h Shellharbour and Nowra
- 98km/h Kiama
- 95km/h Montague Island Lighthouse
- 93km/h Thredbo Top Station
That’s right, locations on the Illawarra coast and adjacent inland have had stronger winds than an exposed lighthouse and the most elevated weather station in Australia at 1957m.
The powerful wind gusts near Nowra brought down powerlines and caused two fires to start and over 7000 residents to wake up without power this morning.
Those in Sydney and the South Coast of NSW have also had some strong winds. Sydney Airport and Port Kembla have both been dealing with sustained 28 knot winds, proving challenges for flights and ships alike.
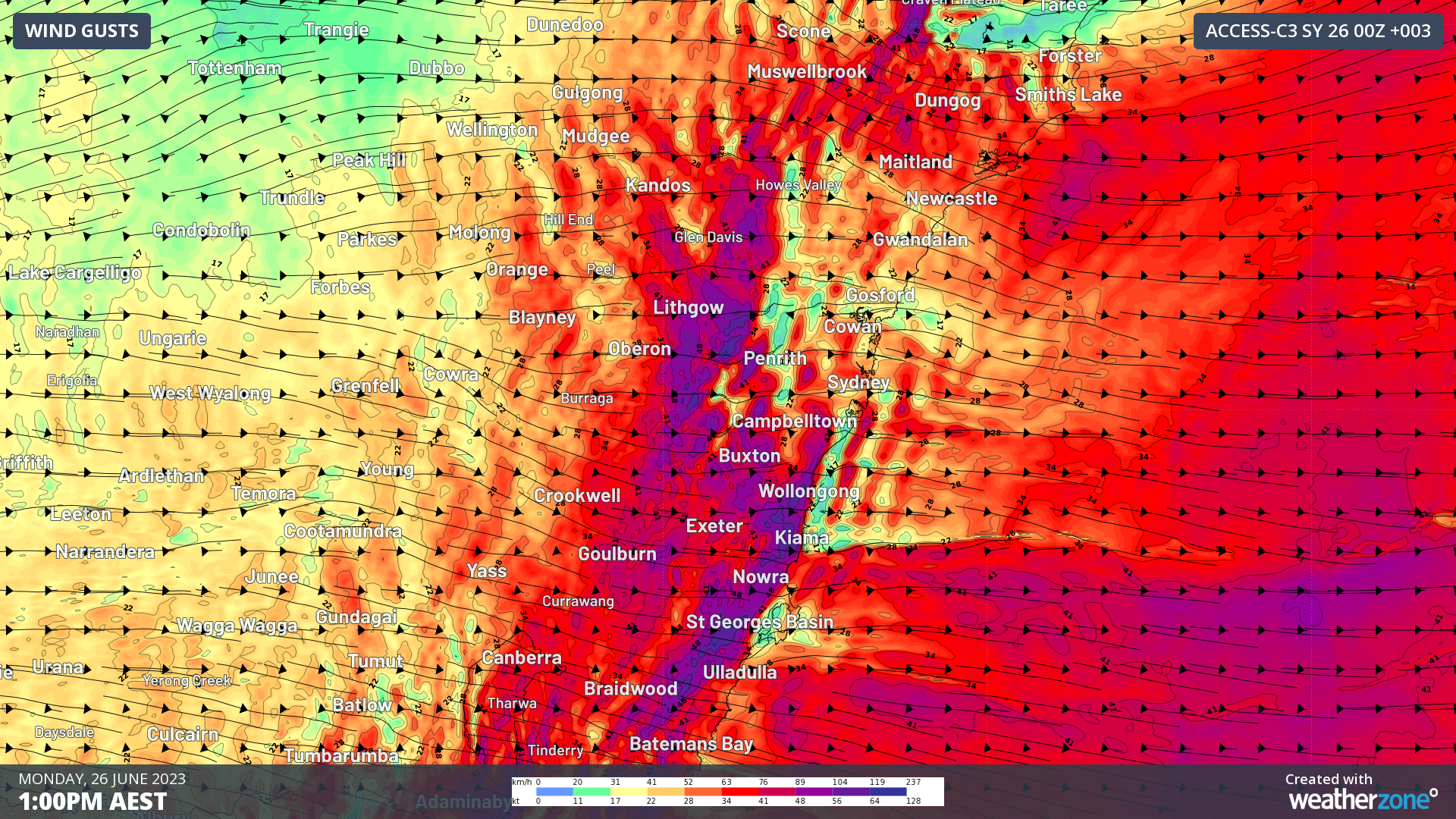
Image: Forecast wind gusts for 1pm Monday. Reds indicate strong winds, with gales in purple
So why are the winds so strong at these normally calmer locations? It’s a process known as the downslope effect.
During the nighttime, the ground cools off faster than the air above it, meaning a temperature inversion forms. This inversion acts a strong barrier, keeping the air above and below it separate from each other. In locations like Sydney and the Illawarra, this inversion will link up to nearby mountain ranges, creating a strong barrier from winds that blow over the mountain.
However, once the sun comes up, it starts to warm the slope of the mountain, allowing the inversion to break down along the slope. With a gap now in the protective inversion, air can rush down the side of the mountains to the ground below. Since the gap in the inversion is small, air rushes down this gap faster than it would otherwise, turning strong winds into gales.
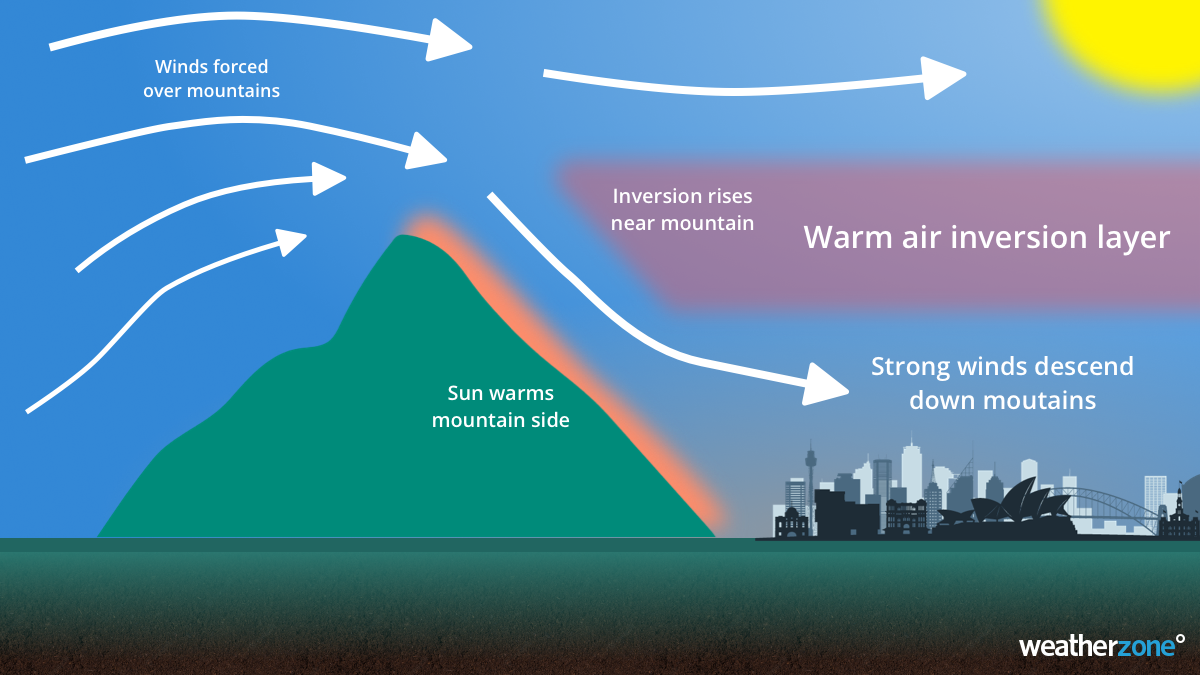
It is somewhat common for this to occur for the NSW east coast, including Sydney and the Illawarra, but this effect occurs throughout Australia anywhere where there is a mountain range. In Adelaide and Perth, this effect occurs in generally easterly winds, while northerly winds trigger the effect for Melbourne and Hobart.
Due to the increase in wind strength on the lee side of mountains, the downslope effect is a critical element in predicting the movements of bushfires, dust storms, air pollution and even blizzards.
The downslope effect has been instrumental in Monday’s powerful winds in NSW, but luckily, the protective inversion will start to build as the sun goes down, causing winds to ease. As the cold front moves further out to sea, high pressure will build, allowing calmer conditions to return.
DTN APAC mixes our expert knowledge, data inflows and artificial intelligence to convert our weather forecasts into a forecast of power outages through our Storm Impact Analytics (SIA). This system compares historical outages with a custom high-resolution forecast to determine where, when and how many power outages are expected during an event. To find out more about our services, please email us at apac.sales@dtn.com.