Nodes of polar air could soon be sweeping around the Southern Hemisphere as tropospheric weather patterns respond to recent warming in the stratosphere above Antarctica.
Over the past fortnight, a pool of abnormally warm air disrupted the shape of the Southern Hemisphere’s stratospheric polar vortex. This phenomenon, which is called sudden stratospheric warming (SSW), occurred around 30 to 40km above Earth’s surface.
While this stratospheric warming occurred a long way above the ground, there are signs that its influence is now filtering downwards through the atmosphere and impacting weather patterns closer to the surface.
What is SSW and how does it impact weather near the ground?
Sudden stratospheric warming (SSW) refers to an abrupt increase in air temperature high above either of Earth’s polar regions. This warming occurs in a layer of the atmosphere called the stratosphere, roughly 30 to 40km above the surface.
Warming in the polar stratosphere during winter and spring can cause the tropospheric polar vortex, which is located closer to the ground, to weaken and become distorted. This weakening of the tropospheric polar vortex typically triggers a negative Southern Annular Mode (SAM) phase, which causes westerly winds and polar air to drift further away from Antarctica and spread towards the mid-latitudes.
The SAM is a key climate driver for Australia and when it is in a negative phase during winter, Australia is more likely to see:
- More cold fronts and low pressure systems over southern Australia
- Increased rainfall and snow potential in southwest and southeast Australia
- Reduced rainfall in parts of eastern Australia
- Stronger winds in the southern half of Australia
In addition to causing cold air to spread further away from Antarctica, a wakened polar vortex can also cause the Southern Hemisphere’s polar jet stream to become more wavy than usual. This wavy pattern, which is called a meridional flow, causes the jet stream to meander as it flows around Antarctica. A wavy polar jet typically causes cold air to venture away from Antarctica in large blobs, which can lead to wintry outbreaks in areas of the mid-latitudes that find themselves under one of these stray pools of polar air.
Negative SAM emerging
The SAM has started to shift into a negative phase this week, likely in response to the recent stratospheric warming. Some forecast models suggest that this negative SAM will strengthen through the end of July and persist into early August.
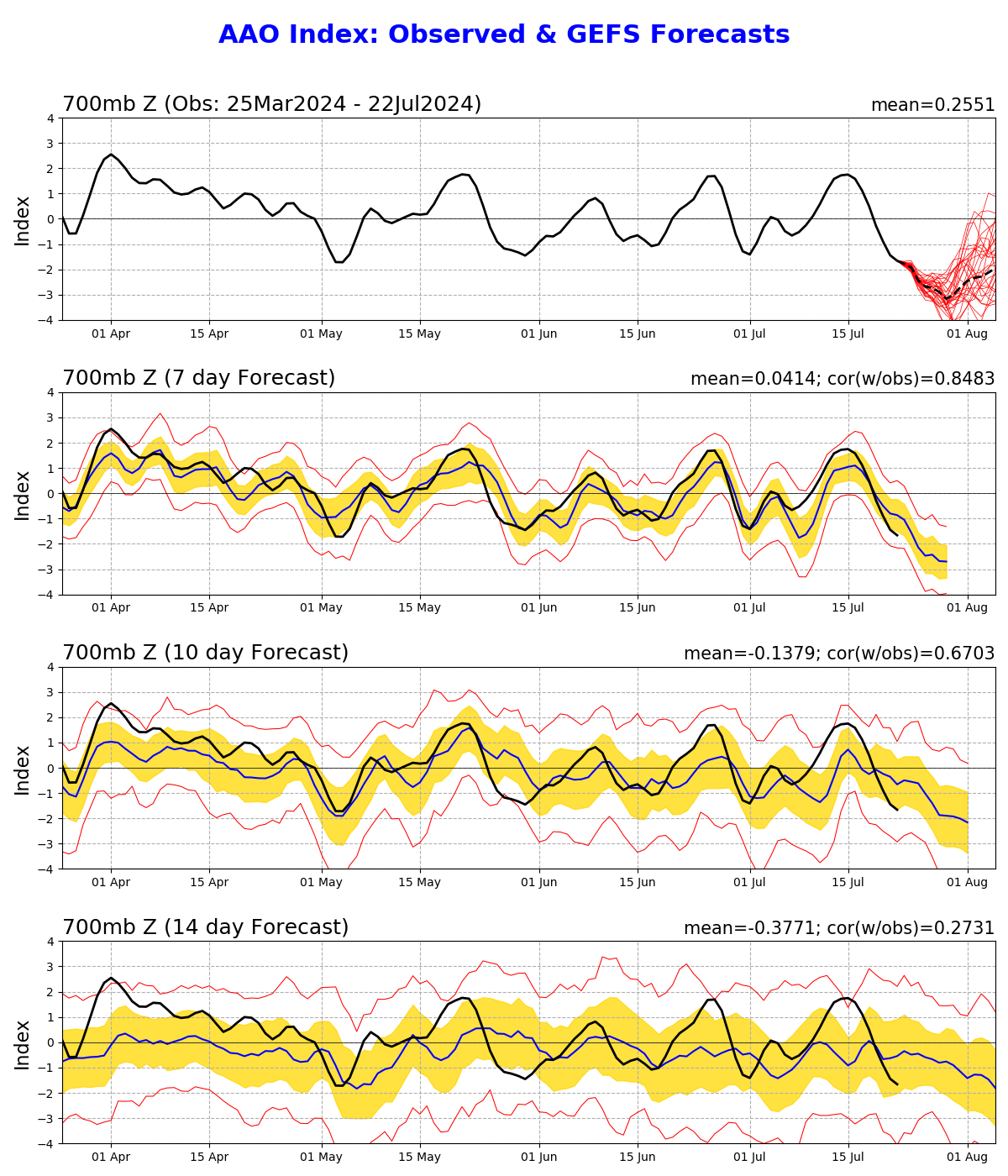
Image: SAM (also called Australian Antarctic Oscillation or AAO) observations and forecast from the GFS model, showing a strengthening negative phase in late July.
In addition to this negative SAM signal, forecast models also anticipate a wavy jet stream will be meandering around the Southern Hemisphere as we head into August.
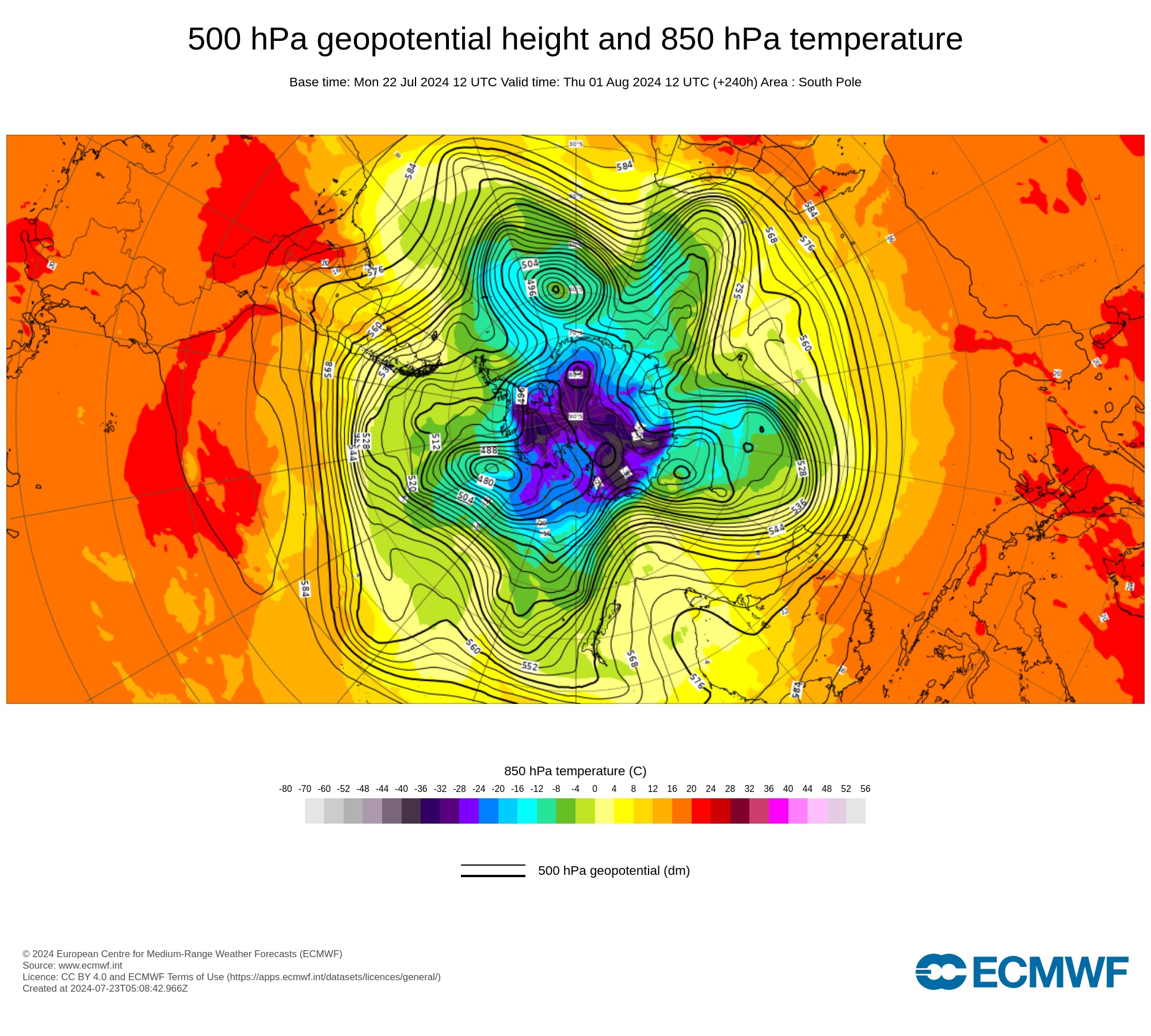
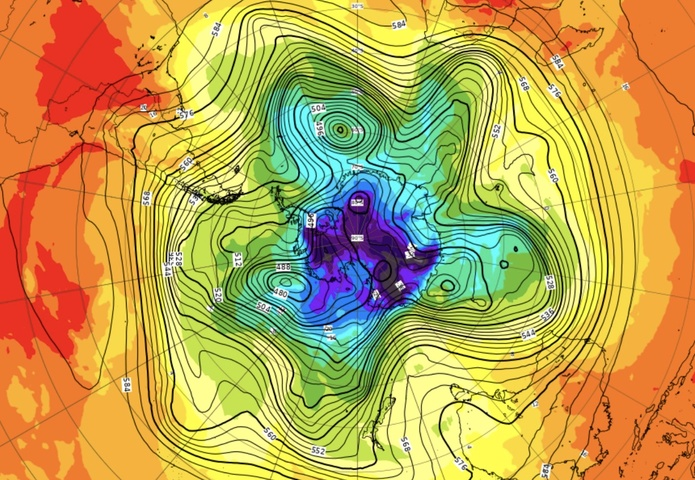
Image: Modelled 500hPa geopotential height and 850hPa temperature over the South Pole on August 1, according to the ECWMF model, showing a meridional pattern with nodes of cold air venturing into the mid-latitudes.
The fingerprints of a negative SAM and wavy polar jet are clear to see in Australia’s weather forecast over the coming fortnight:
- At least three cold fronts will sweep over southern Australia in the next 10 days.
- These fontal systems will cause wind to increase and temperatures to drop over southern parts of the country.
- Rain will be frequent and heavy in parts of southwestern WA and western Tas.
- By contrast, dry and warm continental air will flow over eastern Australia, causing a run of dry and warmer-than-average days on the country’s east coast.
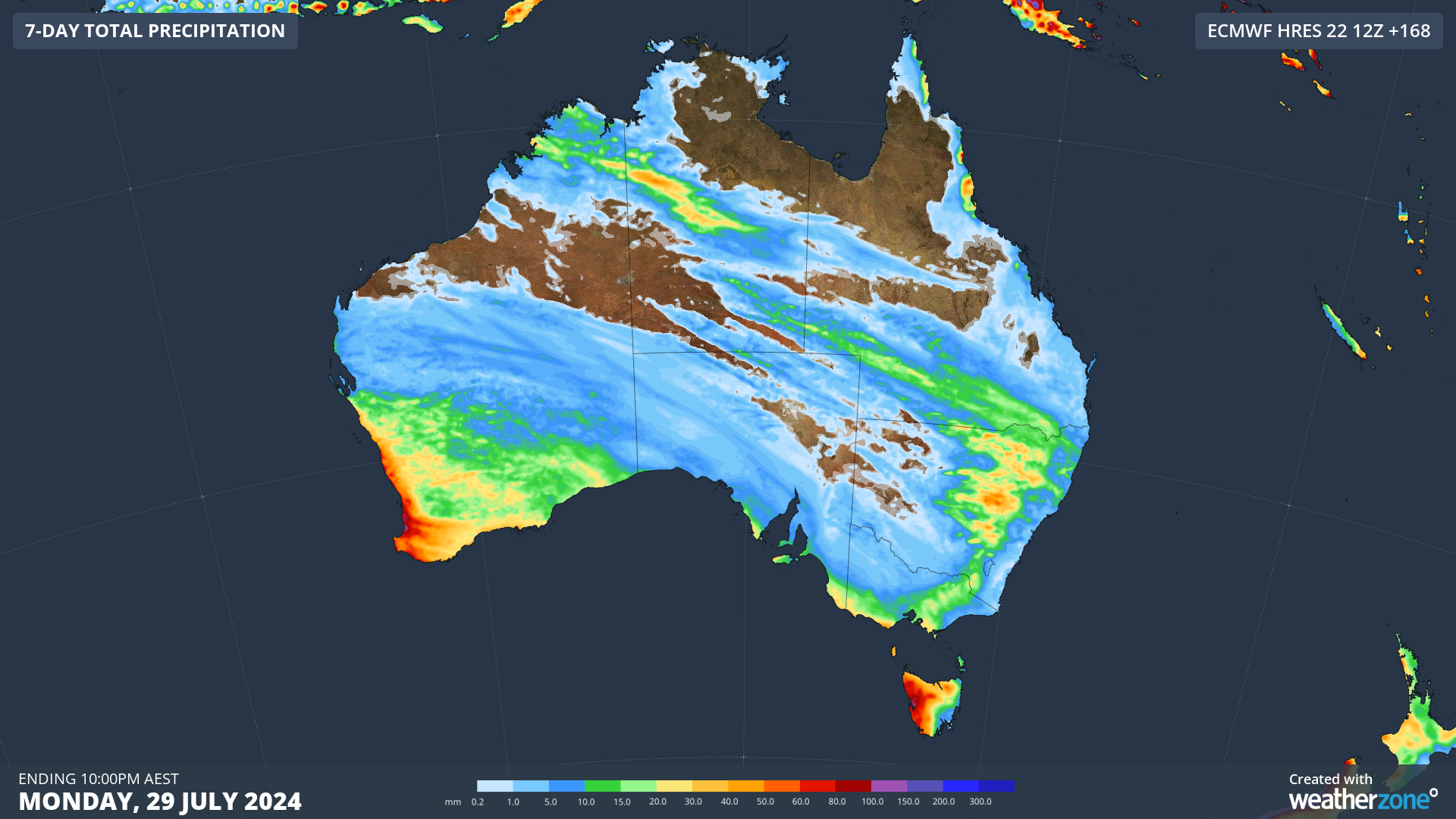
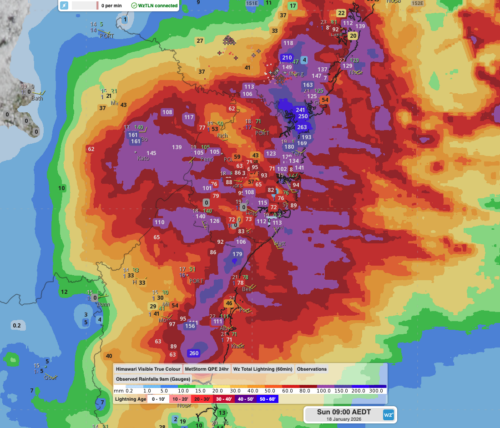
Image: Forecast accumulated rain over Australia during the next seven days combined, according to the ECMWF model.
Looking ahead, there are signs that another period of stratospheric warming could occur above Antarctica in the last week of July. If this does happen, it will increase the likelihood of more negative SAM phases in late winter and early spring.
DTN APAC is a diverse team, with global forecasting, product development and analytics expertise. Couple this with extensive industry experience spanning Aviation to Energy, and we are primed to assist you in strengthening your response to weather
impact.
We work hard to identify your operational pressures and tailor our services and products to meet your needs. Concise communication, giving you full situational awareness exactly when you need it, is our focus. We want to reduce weather risk in your operations, every day.
We deliver clear and comprehensive weather data, personalised risk assessments and briefings to you and your team, so that your critical decisions can be made with confidence.
We are available 365 days a year, so you always have the timely guidance you require, especially when severe conditions hit.
You have our insights to rely on to see you through complex situations, minimising potential loss of profit and maximising the safety of your staff and assets. To find out more, please visit our contact page or email us at apac.sales@dtn.com.