This article was written for April Fools Day. It is not factual.
A new category will be added to the Fujita scale from 2026 to formally recognise the ‘mini tornado’.
The Fujita scale, and the revised Enhanced Fujita scale, are widely accepted scales used for rating tornado intensity. They both use damage assessments from past tornadoes to officially rate their intensity on a six-tiered scale ranging from zero to five, with five being the strongest and zero the weakest.
However, new research points out that growing use of the term ‘mini tornado’, primarily seen on social media and in mainstream media, clearly highlights the need for a new category on the scale.
The pioneering study published in the Journal of Kinetic Energy puts forward a compelling case for including ‘mini tornado’ as an official category on the Fujita and Enhanced Fujita scales globally.
“Research shows us that people like to use the term ‘tornado’ when they talk about any type of strong wind event,” says Dr. Sloof Lirpa, the study’s lead author.
“But we also know that meteorologists can be quite stubborn when it comes to technical weather terms. They really only want to use the word tornado for a tornado, or typhoon for a typhoon, but that doesn’t have to be the case.” says Dr. Lirpa.
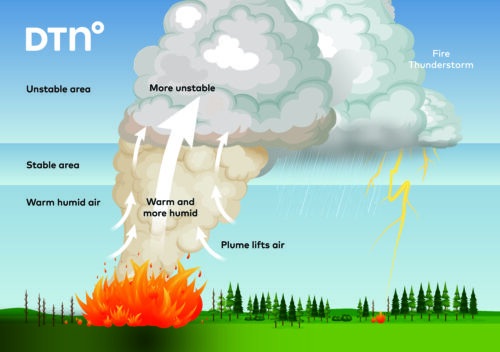
Tornadoes are currently defined as a violently rotating column of air that is touching the ground and attached to the base of a thunderstorm.
In recent years, the term mini tornado has been used erroneously to describe some non-tornadic wind events, including microbursts, squall lines, landspouts and dust devils.

Image: Was that a mini tornado?
The study calls for that meteorologists do away with their strict technical definitions and agree to start using mini tornado officially.
The paper also suggests avoiding red and blue colours on weather maps because they are causing too many arguments on social media.
Note to media: You are welcome to republish text from the above news article as direct quotes from DTN APAC. When doing so, please reference www.apac.dtn.com in the credit.