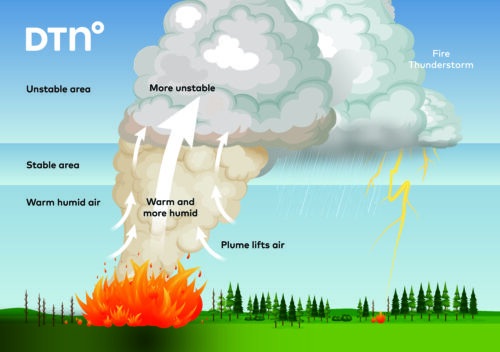
Winds are a key component to understanding the behaviour of bushfires. But what happens when the wind suddenly changes direction?
Typically, a fire will tend to spread along the same direction as the prevailing winds. In a strong wind, this allows the fire front to follow the wind very quickly and can exceed 50km/h in the right conditions. Since following the wind is so favourable in these conditions, the fire width (the distance between the right and left flanks) tends to be quite narrow, while the area burnt can be very long.
When a strong wind change comes in, the fire front will want to change to move in the same direction as the new winds. To achieve this, the fire flanks now become the new fire front. In a rapid change, such as a southerly buster after a day of gusty northwesterly winds, the fire front can become many times larger in a matter of minutes as the fire aligns to the new direction. The type of wind changes that cause this effect are usually those from cold fronts, but those from sea breezes and adiabatic winds off mountains can also drastically change a fire’s movement.
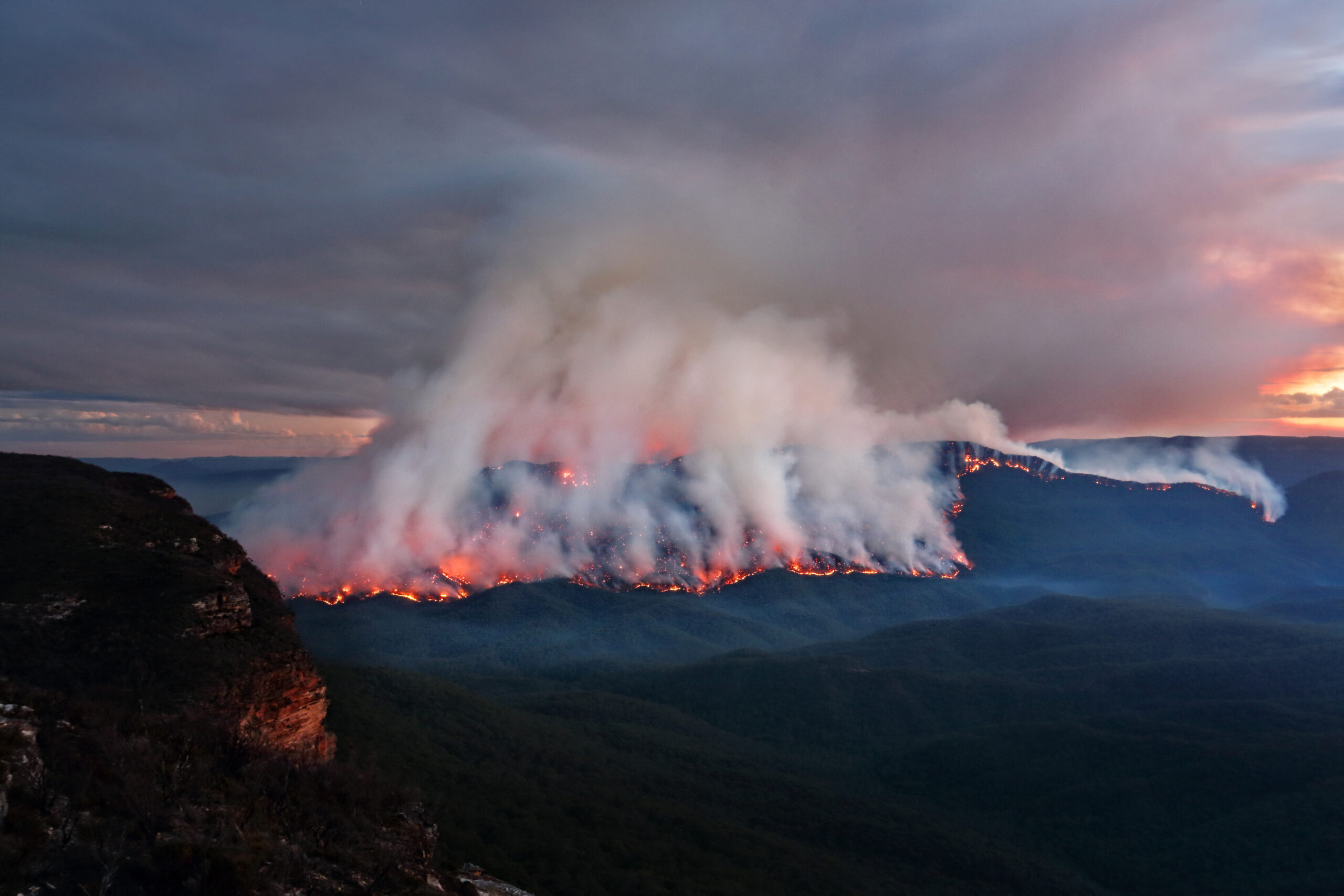
This effect was illustrated clearly on Monday by the Willi Willi Road bushfire at Moparrabah near Kempsey, NSW. The following video shows how the fire and smoke trail grew in a narrow (approx. 4km) strip on Monday in the northwesterly winds, before a strong southerly moved in, turning the fire direction and making it several times wider (approx. 20km) than before.
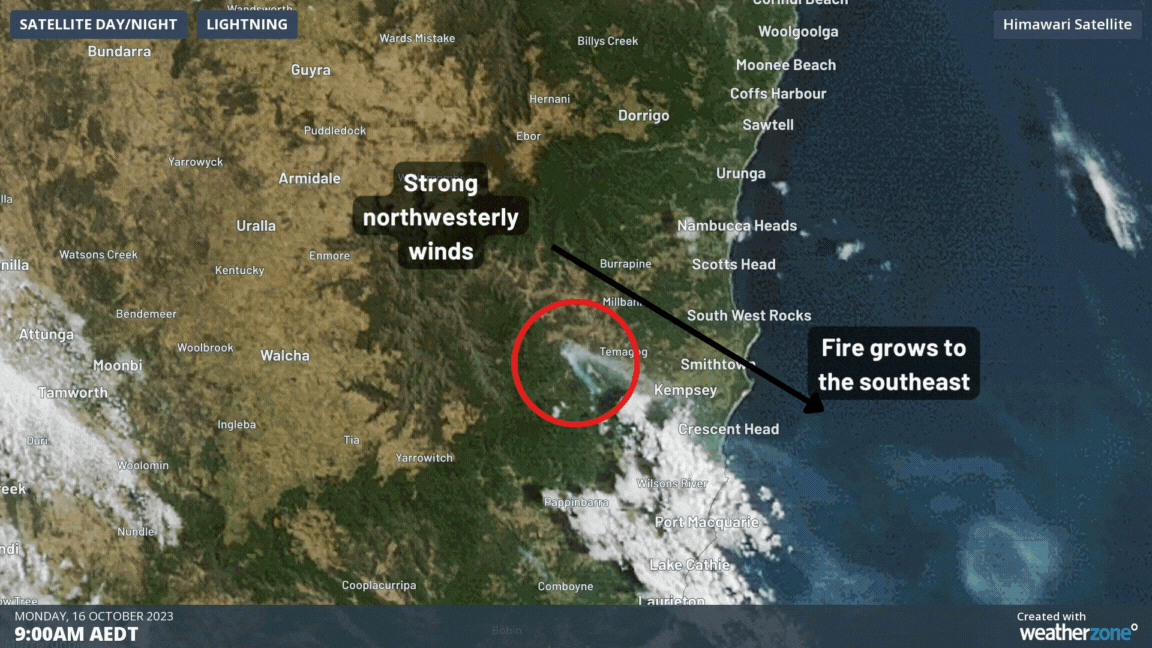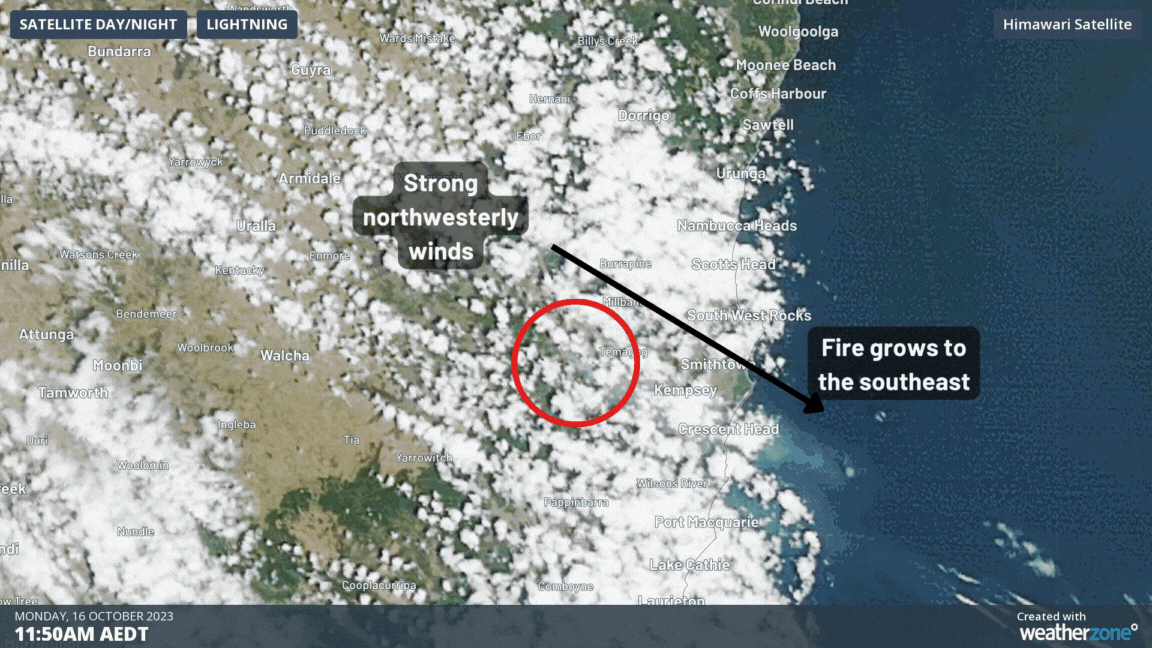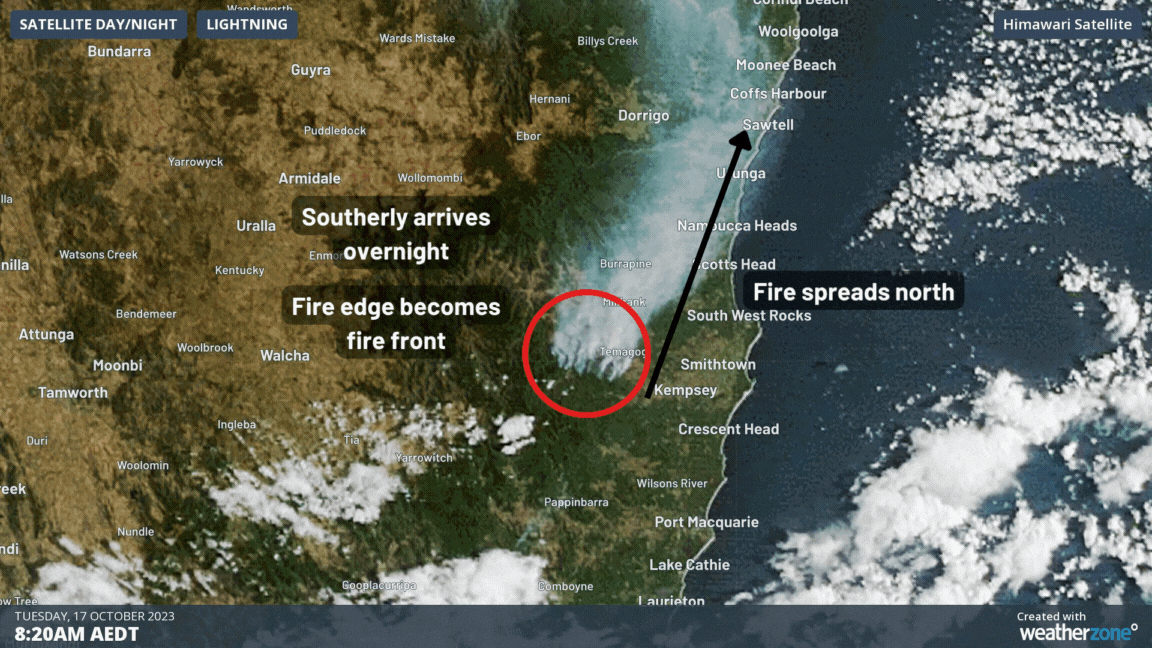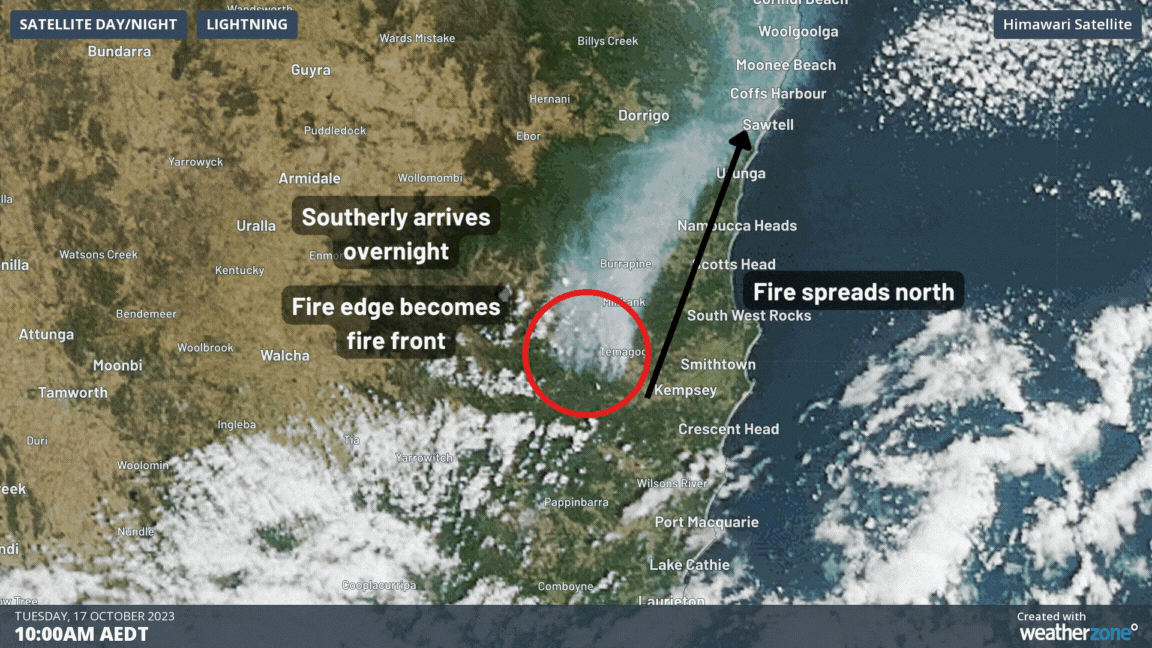
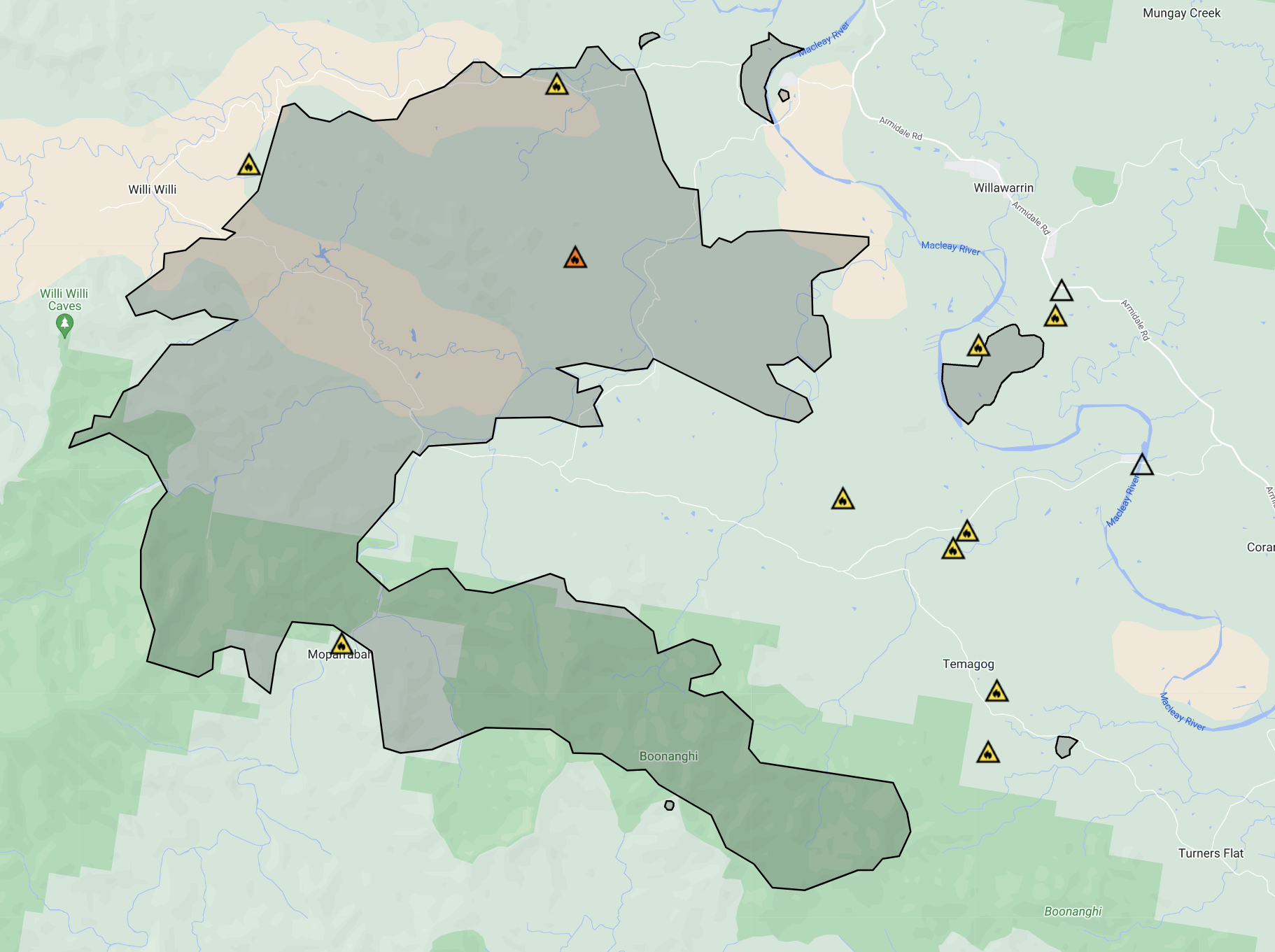
The burnt out area from the NSW RFS shows how the main bushfire front to the south burnt out a long but narrow section of land on Monday afternoon. After the southerly, the left flank of the burnt area has become the new fire front.
While conditions have eased overnight, firefighters will work throughout the day to establish containment lines around a large number of fires.This footage from the Willi Willi Rd Fire was captured last night, as strong southerly winds impacted the fire ground. pic.twitter.com/rkV4EqZKS0
— NSW RFS (@NSWRFS) October 16, 2023
The wind change effect becomes more dramatic the stronger the winds are before the change, not necessarily after it. The longer the fire becomes before the change, the wider it will be after the wind comes through. Since the change occurs so rapidly, it can easily trap firefighters, locals and animals that are not expecting it, and unfortunately has caused hundreds of deaths over Australia’s history. Virtually all of the worst and deadliest fires in Australia’s history, like Black Friday (1939), Ash Wednesday (1983), Black Saturday (2009), and multiple days during Black Summer (2019-20), all featured wind changes that caused the fire front to rapidly grow.
While conditions can be treacherous in the first few hours of a strong wind change, winds do tend to weaken slowly in the days that follow it, with cooler conditions helping to bring the fire back under control.
To find out more about out fire prediction and alerting services, please explore our website or email us at apac.sales@dtn.com.