Parts of central Queensland just received over a month’s rain in 24 hours, with more wet and cold weather on the way in the next few days.
A low pressure trough located over QLD is drawing moisture-laden air from the Coral Sea, leading to widespread cloud and rain over central parts of the state.
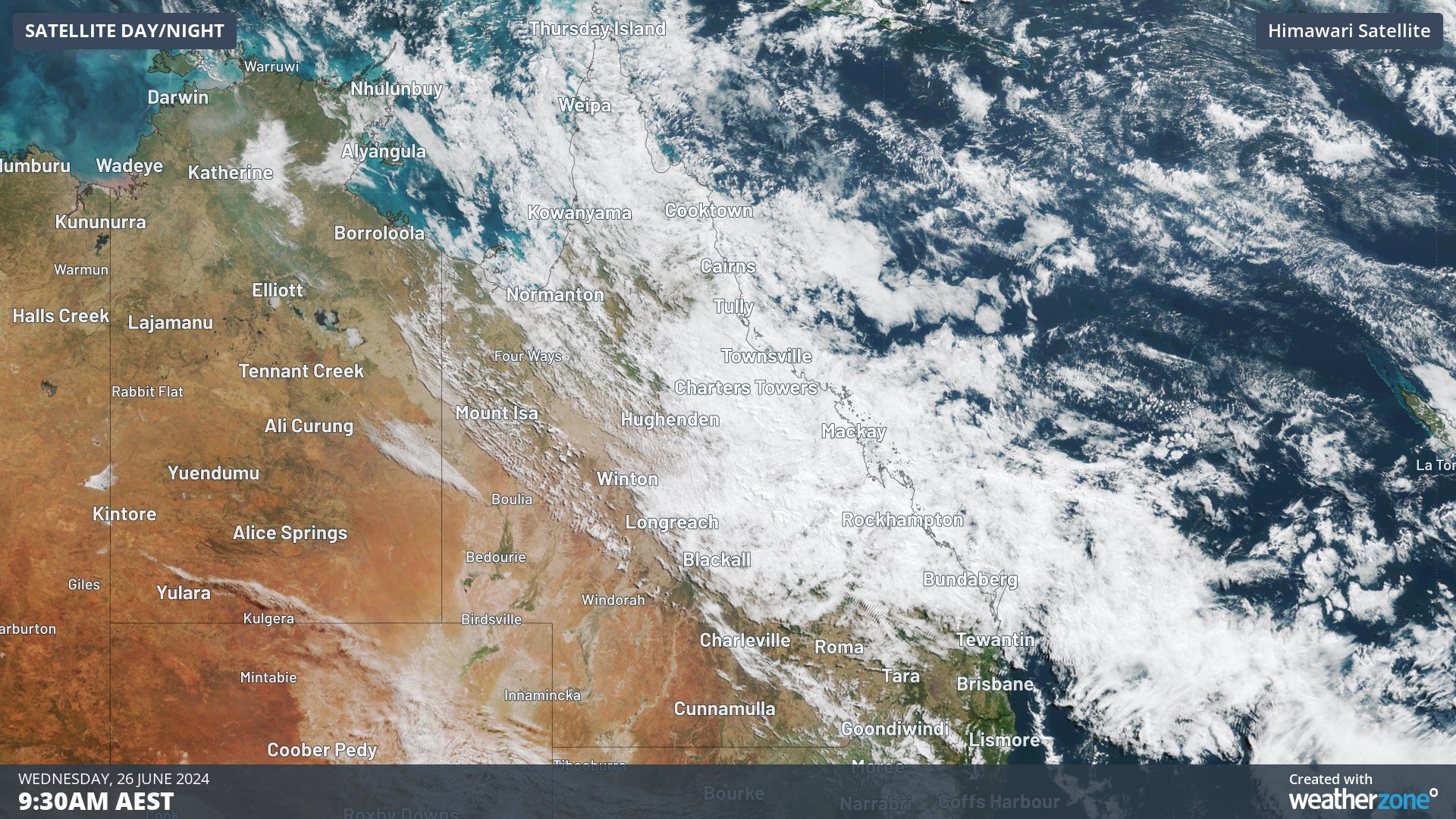
Image: Visible satellite image from Wednesday morning showing cloud over central Qld.
In the 24 hours to 9am on Wednesday, falls of 30 to 60mm were recorded between Mackay and Townsville. This included 59.8mm at Mackay Airport and 55mm at Eungella Dam.
Mackay’s long-term monthly average for June is 59.5mm, making the 59.8mm that fell during the last 24 hours equivalent to an entire month’s rain at this time of year. It was also Mackay’s wettest June day in 21 years.
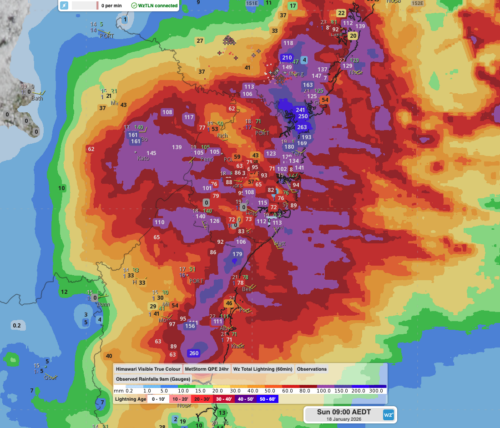
The trough will continue to produce widespread cloud and rain over central Qld on Wednesday and Thursday, with some showers also extending to the state’s north and southeast. The map below shows how much rain one computer model is predicting over Qld on Wednesday and Thursday combined.

Image: Forecast accumulated rain during the 48 hours ending at 10pm AEST on Thursday, June 26.
Rain will start to ease from Friday as the trough weakens, although showers will linger over some parts of the state through the rest of this week.
There are also signs that another band of rain could develop over southern Qld from Sunday into the start of next week as a northwest cloudband drifts across eastern Australia. The days of thick cloud forecast, will likely reduce solar output across Qld.
Weatherzone Business and Solcast are a market-leading partnership delivering highly specialised solar data to the Australian renewable energy industry.
Designed for utility scale solar sites, we offer you a globally proven solution.
With low upfront CAPEX and powerful cloud-based information systems, you can access a complete suite of irradiance and weather data to ensure forecast accuracy and improve site efficiency.
Solcast is the world leader in real-time actuals and rapid-update solar forecasts. This solution utilises Solcast’s centralised Amazon Web Services’ (AWS) cloud infrastructure for all complex algorithmic processes and data plumbing. You will gain the power of AWS to interpret and deliver your data at top speed, providing real-time, historical and forecasting estimates direct to your API.
Receive monitoring and support from the Weatherzone and Solcast teams, 24/7. To find out more, please contact us at apac.sales@dtn.com.